|
|
|
Main Menu
|
|
Sections
Talkback
Downloads
Information
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
This is a new contributed topic summarizing the laws of Physics.
more to come...
- Newton's first, second and third laws of motion
- Euler–Lagrange equation
- Conservation of momentum
- Conservation of mass and energy
- Newton's Law of Gravitation
- Hook's law
- Equivalence of reference systems or coordination frames
- Constancy of the speed of light,
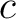
- Einstein's Equivalence of gravitational and inertial mass
- Einstein's Law of Mass-Energy Equivalence
- Einstein–Hilbert action
- Einstein's field equations (EFEs)
- Einstein–Maxwell equations
- Correspondence principle: Newton's law of gravitation derived from EFEs
- Mach's 'principle', or conjecture
- Maupertuis' Principle; Principle of Least (or minimum) Action; Variational principles
- Hamilton's Principle; Principle of Stationary Action
- Snell's Laws
- Huygens's Principle of Diffraction
- Energy Conservation
- Zeroth, First, Second and Third principles of thermodynamics:
Zeroth Law-defines temperature: If a system A is in thermal equilibrium with both systems B and C, then systems B and C are also in thermal equilibrium with each other; that is, if A is at the same temperature as both B and C, then B and C have to be at the same temperature, in thermal equilibrium with each other. First Law: The change in a system's internal energy is equal to the difference between heat added to the system from
its surroundings and work done by the system on its surroundings; Second Law: In any process occurring in a closed system the entropy can only increase; Third Law: the entropy of any pure crystalline system tends to zero in the limit of temperature approaching zero absolute (i.e., in deg Kelvin); also Nernst's law or Nernst heat theorem.
- Avogadro's law: the number of molecules or atoms in a specific volume of gas is a universal constant, independent of their size or the molecular mass of the gas; a mol of gas contains always Avogadro's number,
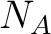 , of molecules of the gas; , of molecules of the gas;
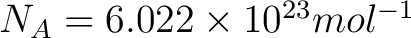 . .
- Clausius–Clapeyron equation
- Van't Hoff equation
- Henry's law: At constant temperature, the amount of a given gas dissolved in a given type and volume of liquid is directly proportional to the partial pressure of that gas in equilibrium with that liquid.
- Dalton's law (Dalton's law of partial pressures): The total pressure exerted by a gaseous mixture is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of each individual component in a gas mixture.
- Van der Waals equation of state: Principle of Corresponding States
- Gibbs–Duhem equation, or the Phase Law
- Gibbs–Helmholtz equations
- Kopp's law for heat capacities
- Ehrenfest equations
- Maxwell's relations for Thermodynamic potentials
- Onsager's Principle; Onsager reciprocal relations
- Stefan–Boltzmann's Law
- Fick's laws of diffusion
- Maxwell—Stefan diffusion
- Churchill-Bernstein Equation
- Raoult's law
- Duhem–Margules equation
- Thermodynamics of black holes and spin networks in Qauntum Gravity
- Maxwell–Boltzmann distribution laws:
- Maxwell—Boltzmann statistics,
- Bose–Einstein statistics,
- Ferm–Dirac statistics,
- Partition function and the Equations of State of a Thermodynamic System
- Schwinger functions and Osterwalder—Schrader theorem in statistical field theory
- Langevin equation
- Planck's law and Universal constant,
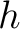
- Einstein's Laws of Light absorption and Emission; Einstein's coefficients
- Law of photoelectric effect
- Quantization Laws
- First and Second quantization Principles
- Correspondence Principle
- wave-particle duality (de Broglie)
- Superposition Principle and the quantum Wavefunction
- Uncertainty Principle (Heisenberg)
- Schr"/odinger's Equations
- Hamilton's Principle
- Einstein–Maxwell–Dirac equations (EMD)
- Klein–Fock–Gordon equation
- Rarita–Schwinger equation for spin–3/2 fermions
- Conservation Laws in Spontaneous and quantum measurement Processes
- Pauli's Principle for fermions
- Goldstone theorem
- Kirchhoff's Laws of spectroscopic analysis: Kirchhoff showed that there are three types of spectra emitted by objects: 1) Continuous spectrum – a solid or liquid body radiates an uninterrupted, smooth spectrum (called a Planck curve); 2) Emission spectrum– a radiating gas produces a spectrum of discrete spectral lines 3) Absorption spectrum – a continuous spectrum that passes through a cool gas has specific spectral lines removed (inverse of an emission spectrum)
- Dispersion laws
- superconductivity principle and Meissner effect
- Wheeler–DeWitt equation in quantum gravity
Principles of quantum field theory (QFT) and quantum electrodynamics (QED)
- Particle Indistinguishability
- Second Quantization
- Mass–renormalization laws
- Schwinger–Dyson equation
more to come...
|
Anyone with an account can edit this entry. Please help improve it!
"physical laws" is owned by bci1.
|
|
See Also: Axioms of Physics
| Also defines: |
physical law, internal energy, energy-momentum tensor, Huygen's principle of diffraction, Bragg's law, Heisenberg Principle, energy-mass equivalence, principle of constancy of light speed, Maxwell's laws, Netwon's laws, Newton's law of gravitation, correspondence principle, Maupertuis's principle, Hamilton's principle, variational principles, wave-particle duality principle, quantization laws, Principle of Corresponding States |
| Keywords: |
law, physical law, physical principle, Huygen's principle of diffraction, Bragg's law, Heisenberg Principle, energy-mass equivalence, principle of constancy of light speed, Maxwell's laws, Netwon's laws, Newton's law of gravitation, correspondence principle, Maupertuis's principle, Hamilton's principle, variational principles, wavge-particle duality principle, quantization laws, principle of corresponding statesPrinciple of Corresponding States |
Cross-references: Goldstone bosons, string theories, supersymmetry, lepton, radioactive decay, QED, quantum electrodynamics, QFT, quantum field theory, quantum gravity, Meissner effect, superconductivity, solid, spectrum, objects, Goldstone theorem, quantum measurement, fermions, wave-particle duality, quantization, photoelectric effect, Planck's law, function, spin networks, black holes, Thermodynamic, relations, Dalton's law, equilibrium, partial pressure, type, universal constant, volume, molecules, theorem, entropy, closed system, work, heat, thermal equilibrium, system, temperature, principles of thermodynamics, Maxwell's equations, Coulomb's law, charge, field, inertial mass, Einstein's, speed of light, reference systems, energy, mass, momentum, motion
There are 18 references to this object.
This is version 83 of physical laws, born on 2010-11-07, modified 2010-11-24.
Object id is 892, canonical name is PhysicalLaws.
Accessed 1674 times total.
Classification:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pending Errata and Addenda
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

