|
In 1895 Heinrich Hertz observed that ultraviolet light from the sparks of his generator for radio waves he had recently discovered, falling on the negative electrode of his radio wave detector, induced the flow of electricity in the gap between the electrodes. Pursuing the phenomenon in detail, he discovered the photoelectric effect whereby light of sufficiently short wavelength causes the ejection of electrons from a metal surface. 1905 Nobel Laureate Philipp Lenard made improved measurements and demonstrated by determination of their charge to mass ratio that the ejected particles are identical with the electrons that had recently been discovered by 1906
Nobel Laureate J. J. Thomson in experiments with cathode rays.
Crude though the early data were, the qualitative fact of the dependence of the critical cutoff voltage on the wavelength of light emerged with sufficient clarity to induce the young Albert Einstein, working as a patent examiner in the Swiss Patent Office in 1905, to link the effect with the recent idea, introduced by Planck in 1900, that matter radiates its energy in quanta of energy 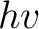 . He postulated that light delivers its energy to an absorber in quanta with energy . He postulated that light delivers its energy to an absorber in quanta with energy 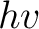 . Thus, if it takes an amount of energy . Thus, if it takes an amount of energy 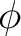 to lift an electron out of the surface and away from its image charge, then the residual kinetic energy to lift an electron out of the surface and away from its image charge, then the residual kinetic energy 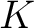 of the ejected electron is of the ejected electron is
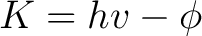 |
(1) |
1921 Nobel Prize was awarded to Albert Einstein for his discovery of "the law of photoelectric effect". It was not until 1912 that the technical problems of making precision measurements of the photoelectric effect were overcome by 1928 Nobel Laureate Sir Owen Wilans Richardson and K. T. Compton to the point where the Einstein photoelectric equation could be tested to high accuracy and used in precise determinations of Planck's Constant
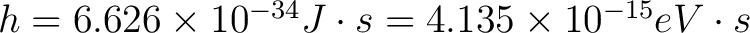
References
This is a derivative work from [1] a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 work.
[1] MIT OpenCourseWare, 8.13-14 Experimental Physics I + II , Fall 2007 - Spring 2008.
| 
