|
Work is defined as the change of kinetic energy of an object caused by a force along a distance.
Work is commonly denoted by the latter 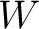
The SI unit for work is joule [J] which is the same as
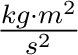 in SI base units. in SI base units.
When focusing on an object moving along a straight line under the effect of constant forces 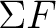 . Let's define a . Let's define a 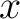 axis along the line of motion. axis along the line of motion.
According to Newton:
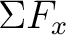 = = 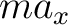
The acceleration 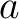 is constant (the sum of forces is constant, and so the following kinematic formula is relevant: is constant (the sum of forces is constant, and so the following kinematic formula is relevant:
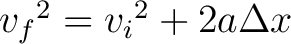 ( (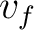 -The final velocity, -The final velocity, 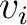 -The initial velocity) -The initial velocity)
When inserting the previous equation into Newton's second law:
And after a few algebric actions we get:
From that we can conclude that
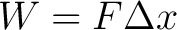 ; ;
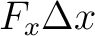 is the work done by the force is the work done by the force 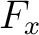 along the route along the route 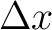
Work like energy is a scalar but is defined as the product of two vectorial parameters:
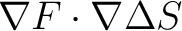 and so in a two dimentional space work is defined as the scalar product of force and so in a two dimentional space work is defined as the scalar product of force 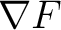 and change in place and change in place
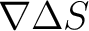 . .
| 
