|
In physics, the resultant force is the single force that represents the combined effect of multiple forces acting on an object. Forces are vector quantities, characterized by both magnitude and direction. To find the resultant force, we add the individual force vectors using vector addition.
Consider an object subjected to two forces:
-
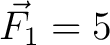 N at N at 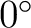 (along the positive (along the positive 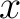 -axis). -axis).
-
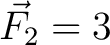 N at N at 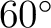 from the positive from the positive 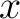 -axis. -axis.
We aim to find the resultant force
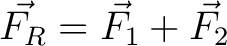 . .
Express each force in terms of its 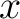 - and - and 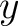 -components: -components:
| 
