|
In mathematical physics, M-theory is a recent extension of five superstring theories, or a relatively recent theory of everything that includes the time evolution through the Big-Bang event that created our Universe. It replaces the older string theory in 10 dimensions with a P-brane theory in 11 dimensions, one time dimension and 10 spatial dimensions. The Big-Bang is hypothesized to occur in M-theory as a result of the collision of two parallel universe P-branes, each with ten spatial dimensions and one temporal dimension. Heterogeneities in the new Universe formed after the collision would be explained by wave-like fluctuations of the two colliding branes. Moreover, a unification of five
previous 10D string theories would occur in this M-theory, or Master theory. Its equations may be then also unified with previous supergravity theory in 11 dimensions.
It has been said that: “The final mathematical formulation of M-theory will have to make contact with the theory of vector bundles, K-theory and noncommutative geometry.”
1. An introduction to string and M-theory for the layman:
2. Robbert Dijkgraaf. The Mathematics of M–Theory.
3. J. Polchinski, Dirichlet–branes and Ramond–Ramond charges, Phys. Rev. Lett. 75 (1995) 4724–4727,
 . .
4 J. Polchinski, String Theory (Cambridge Monographs on Mathematical Physics), Cambridge University Press, 1998.
5. G. Segal, The definition of conformal field theory, preprint; Two dimensional conformal field theories and modular functors, in IXth International Conference on Mathematical Physics,. B. Simon, A. Truman and I. M. Davies Eds. (Adam Hilger, Bristol,1989).
6. N. Seiberg and E. Witten, String theory and noncommutative geometry, JHEP 9909(1999) 032,
 . .
7. A. Sen and B. Zwiebach, Tachyon condensation in string field theory, JHEP 0003 (2000) 002,
 . .
8. Contributed Book, Edited by bci1. M-theory and Supergravity. 372pp, 56Mb ODT doc; 16Mb PDF, April 7, 2010.
9. E. Witten, String theory in various dimensions, Nucl. Phys. B 443 (1995) 85,
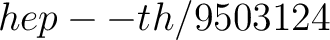 . .
10. E. Witten, Bound states of strings and p–branes, Nucl. Phys. B460 (1996) 335,
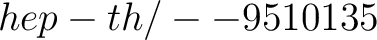 . .
11. E. Witten, D–branes and K–theory, JHEP 9812 (1998) 019,
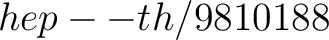 . .
|

