|
generalized Van Kampen theorems (HD-GVKT) -- higher dimensional
|
(Topic)
|
|
|
There are several generalizations of the original van Kampen theorem, such as its extension to crossed complexes, its extension in categorical form in terms of colimits, and its generalization to higher dimensions, i.e., its extension to 2-groupoids, 2-categories and double groupoids [3].
With this HDA-GVKT approach one obtains comparatively quickly not only classical results such as the Brouwer degree and the relative Hurewicz theorem, but also non–commutative results on second relative homotopy groups, as well as higher dimensional results involving the action of, and also presentations of, the fundamental group. For example, the fundamental crossed complex 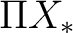 of the skeletal filtration of a of the skeletal filtration of a  –complex –complex  is a useful generalization of the usual cellular chains of the universal cover of is a useful generalization of the usual cellular chains of the universal cover of  . It also gives a replacement for singular chains by taking . It also gives a replacement for singular chains by taking  to be the geometric realization of a singular complex of a space. Non-Abelian higher homotopy (and homology) results in higher dimensional algebra (HDA) were proven by Ronald Brown that generalize the original van Kampen's theorem for fundamental groups (ordinary homotopy, [10]) to fundamental groupoids ([1]) double groupoids, and higher homotopy ([7]); please see also Ronald Brown's presentation of the original van Kampen's theorem at PlanetMath.org [8]. to be the geometric realization of a singular complex of a space. Non-Abelian higher homotopy (and homology) results in higher dimensional algebra (HDA) were proven by Ronald Brown that generalize the original van Kampen's theorem for fundamental groups (ordinary homotopy, [10]) to fundamental groupoids ([1]) double groupoids, and higher homotopy ([7]); please see also Ronald Brown's presentation of the original van Kampen's theorem at PlanetMath.org [8].
Related research areas are: algebraic topology, higher dimensional algebra (HDA) , higher dimensional homotopy, non-Abelian homology theory, supercategories, axiomatic theory of supercategories, n-categories, lextensive categories, topoi/toposes, double groupoids, omega-groupoids, crossed complexes of groupoids, double categories, double algebroids, categorical ontology, axiomatic foundations of Mathematics, and so on.
Its potential for applications in Quantum Algebraic Topology (QAT), and especially in Non-Abelian Quantum Algebraic Topology (NAQAT) related to QFT, HQFT, TQFT, quantum gravity and supergravity (quantum field) theories has also been recently pointed out and explored ([9,11,13]).
Consideration of a set of base points leads next to the following theorem for the fundamental groupoid.
Let the space  be the union of open sets be the union of open sets  with intersection with intersection  , and let , and let  be a subset of be a subset of  meeting each path component of meeting each path component of  . Then: . Then:
is a pushout of groupoids
When extended to the context of double groupoids this theorem leads to a higher dimensional generalization of the Van Kampen theorem, the HD-GVKT, [3].
Note that this theorem is a generalization of an analogous Van Kampen theorem for the fundamental group, [1,10]. From this theorem, one can compute a particular fundamental group
 using combinatorial information on the graph of intersections of path components of using combinatorial information on the graph of intersections of path components of  , but for this it is useful to develop the algebra of groupoids. Notice two special features of this result: , but for this it is useful to develop the algebra of groupoids. Notice two special features of this result:
- (i) The computation of the invariant one wants to obtain, the fundamental group, is obtained from the computation of a larger structure, and so part of the work is to give methods for computing the smaller structure from the larger one. This usually involves non canonical choices, such as that of a maximal tree in a connected graph. The work on applying groupoids to groups gives many examples of such methods [6,7].
- (ii) The fact that the computation can be done at all is surprising in two ways: (a) The fundamental group is computed precisely, even though the information for it uses input in two dimensions, namely 0 and 1. This is contrary to the experience in homological algebra and algebraic topology, where the interaction of several dimensions involves exact sequences or spectral sequences, which give information only up to extension, and (b) the result is a non commutative invariant, which is usually even more difficult to compute precisely.
The reason for this success seems to be that the fundamental groupoid
 contains information in dimensions 0 and 1, and therefore it can adequately reflect the geometry of the intersections of the path components of contains information in dimensions 0 and 1, and therefore it can adequately reflect the geometry of the intersections of the path components of  and the morphisms induced by the inclusions of and the morphisms induced by the inclusions of  in in  and and  . This fact also suggested the question of whether such methods could be extended successfully to higher dimensions. . This fact also suggested the question of whether such methods could be extended successfully to higher dimensions.
- 1
- R. Brown, Groupoids and Van Kampen's theorem., Proc. London Math. Soc. (3) 17 (1967) 385-401.
- 2
- R. Brown, Topology and Groupoids., Booksurge PLC (2006).
- 3
- R. Brown, K.A. Hardie, K.H. Kamps and T. Porter, A homotopy double groupoid of a Hausdorff space, Theory and Applications of Categories. 10 (2002) 71-93.
- 4
- R. Brown and A. Razak, A Van Kampen theorem for unions of non-connected spaces, Archiv. Math. 42 (1984) 85-88.
- 5
- R. Brown and G. Janelidze.:1997, Van Kampen theorems for categories of covering morphisms in lextensive categories, J. Pure Appl. Algebra, 119: 255–263, ISSN 0022-4049.
- 6
- P.J. Higgins, Categories and Groupoids, van Nostrand: New York, 1971; also Reprints of Theory and Applications of Categories, No. 7 (2005) pp 1-195.
- 7
- Brown R., Higgins P.J., Sivera, R. (2008), Non-Abelian algebraic topology, (in preparation)., available here as a PDF; PDFs of other relevant HDA papers .
- 8
- R. Brown: VanKampen-sTheorem
- 9
- Brown, R., Glazebrook, J. F. and I.C. Baianu.(2007), A Conceptual, Categorical and Higher Dimensional Algebra Framework of Universal Ontology and the Theory of Levels for Highly Complex Structures and Dynamics., Axiomathes (17): 321–379.
- 10
- van Kampen, E. H. (1933), On the Connection Between the Fundamental Groups of some Related Spaces, Amer. J. Math. 55: 261–267.
- 11
- Baianu I. C., Brown R., Georgescu G. and J. F. Glazebrook.(2006), Complex Nonlinear Biodynamics in Categories, Higher Dimensional Algebra and Łukasiewicz–Moisil Topos: Transformations of Neuronal, Genetic and Neoplastic Networks., Axiomathes, 16 Nos. 1–2: 65–122.
- 12
- Baianu, I.C., R. Brown and J. F. Glazebrook.(2007), A Non-Abelian, Categorical Ontology of Spacetimes and Quantum Gravity, Axiomathes, 17: 169-225.
- 13
- Baianu, I. C., Brown, R. and J. F. Glazebrook.(2008), Quantum Algebraic Topology and Field Theories., pp.145, the Monograph's PDF is here available(Preprint).
|
"generalized Van Kampen theorems (HD-GVKT) -- higher dimensional" is owned by bci1.
|
|
See Also: Van Kampen Theorem for groups and groupoids
| Other names: |
HD-GvKT /Van Kampen theorems |
| Also defines: |
generalized Van Kampen theorems, HD-GvKT, fundamental crossed complex, fundamental group, homotopy group, universal cover, universal chains, singular chains, higher dimensional homotopy, non-Abelian higher homotopy, nonabelian higher homotopy, omega-groupoids, Brouwer degree, crossed complexes, GvKT, NAQAT, non-Abelian Quantum Algebraic Topology, singular complex of a space |
| Keywords: |
higher dimensional, generalized van Kampen theorems (HD-GVKT) |
Cross-references: groups, tree, work, computation, graph, pushout, morphisms, diagram, isomorphism, union, quantum field, supergravity, quantum gravity, TQFT, HQFT, QFT, Non-Abelian Quantum Algebraic Topology, QAT, Quantum Algebraic Topology, categorical ontology, double algebroids, double categories, groupoids, categories, n-categories, supercategories, homology theory, non-Abelian, algebraic topology, higher homotopy, fundamental groupoids, homotopy, fundamental groups, theorem, Ronald Brown, HDA, higher dimensional algebra, homotopy groups, relative Hurewicz theorem, double groupoids, 2-categories, 2-groupoids
There are 21 references to this object.
This is version 10 of generalized Van Kampen theorems (HD-GVKT) -- higher dimensional, born on 2009-05-01, modified 2010-12-13.
Object id is 706, canonical name is GeneralizedVanKampenTheoremsHDGVKT.
Accessed 10667 times total.
Classification:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pending Errata and Addenda
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

