|
Given a plane curve 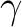 , its catacaustic (Greek , its catacaustic (Greek
 `burning along') is the envelope of a family of light rays reflected from `burning along') is the envelope of a family of light rays reflected from  after having emanated from a fixed point (which may be infinitely far, in which case the rays are initially parallel). after having emanated from a fixed point (which may be infinitely far, in which case the rays are initially parallel).
For example, the catacaustic of a logarithmic spiral reflecting the rays emanating from the origin is a congruent spiral. The catacaustic of the exponential curve 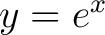 reflecting the vertical rays reflecting the vertical rays 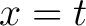 is the catenary is the catenary
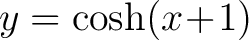 . .
| 
