|
Let
where the 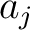 's are real numbers satisfying 's are real numbers satisfying
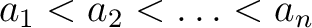 , the , the 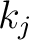 's are real numbers satisfying 's are real numbers satisfying
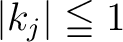 ; the integral expression means a complex antiderivative, ; the integral expression means a complex antiderivative, 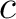 and and 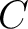 are complex constants. are complex constants.
The transformation
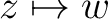 maps the real axis and the upper half-plane conformally onto the closed area bounded by a broken line. Some vertices of this line may be in the infinity (the corresponding angles are = 0). When maps the real axis and the upper half-plane conformally onto the closed area bounded by a broken line. Some vertices of this line may be in the infinity (the corresponding angles are = 0). When 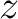 moves on the real axis from moves on the real axis from 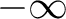 to to 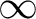 , , 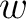 moves along the broken line so that the direction turns the amount moves along the broken line so that the direction turns the amount 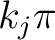 anticlockwise every time anticlockwise every time
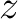 passes a point passes a point 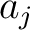 . If the broken line closes to a polygon, then . If the broken line closes to a polygon, then
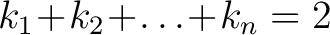 . .
This transformation is used in solving two-dimensional potential problems. The parameters 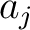 and and 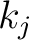 are chosen such that the given polygonal domain in the complex are chosen such that the given polygonal domain in the complex 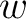 -plane can be obtained. -plane can be obtained.
A half-trivial example of the transformation is
which maps the upper half-plane onto the first quadrant of the complex plane.
| 
