|
Quantum topological order and extended quantum symmetries
|
(Topic)
|
|
|
In noncrystalline systems and certain quantum (Hall) liquids with long-range coupling symmetry-breaking descriptions of phase transitions were suggested to be insufficient, and alternative theories in terms of topological order were proposed to replace previous Landau symmetry-breaking models. Such glassy systems with short-range structural order, but long-range correlations in magnetic and/or electrical properties may thus exhibit several topological orders both in lower and higher dimensions. Quantum states with different topological orders can be interchanged only through a (quantum) phase transition– a result that should be provable by means of Quantum Algebraic Topology means in terms of quantum operator algebras and locally compact quantum groupoid representations [15]. On the other hand, spontaneous symmetry-breaking is known to involve the generation of Goldstone bosons according to the well-known Goldstone theorem [21]; thus, low temperature superconductivity is known to occur via the generation of (electron) Cooper pairs (phonon-coupled to the lattice ions)–that are Goldstone bosons of spin-0– with long-range correlations and quantum coherence throughout the quantum superconductor. Thus, the superconductivity phase transition
involves a change from Fermi statistics for electrons in the metal at temperature above 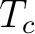 to Bose-Einstein statsistics for the Cooper pairs that are responsible for superconductivity at the lower temperatures to Bose-Einstein statsistics for the Cooper pairs that are responsible for superconductivity at the lower temperatures 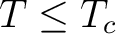 . Despite considerable theoretical and experimental efforts, prior to 2009 the appropriate algebraic topological structures responsible for quantum topological orders have not been either classified or identified. What has become however abundantly clear since the work of Sir Neville F. Mott, P.W. Anderson, Steve Weinberg, John Van Vleck, Sir Michael Atyiah, van 't Hooft, E. Witten, Turaev, K. Porter, L. Vainerman, Isham, M. Levin, X-G. Wen , Y.K. Levine, A. Tijon, and many other quantum theoretical physicists, is that quantum algebraic topology approaches are key to understanding long-range order correlations, the effects of partial disorder in solids and the emergence of extended quantum symmetry in many-body systems and quantum field theories (QFT), including quantum gravity (QG). . Despite considerable theoretical and experimental efforts, prior to 2009 the appropriate algebraic topological structures responsible for quantum topological orders have not been either classified or identified. What has become however abundantly clear since the work of Sir Neville F. Mott, P.W. Anderson, Steve Weinberg, John Van Vleck, Sir Michael Atyiah, van 't Hooft, E. Witten, Turaev, K. Porter, L. Vainerman, Isham, M. Levin, X-G. Wen , Y.K. Levine, A. Tijon, and many other quantum theoretical physicists, is that quantum algebraic topology approaches are key to understanding long-range order correlations, the effects of partial disorder in solids and the emergence of extended quantum symmetry in many-body systems and quantum field theories (QFT), including quantum gravity (QG).
A basic concept in topological order theories is that of an ordered, entangled ground state for a many-body system with long-range coupling(s) (as for example magnetic dipole-dipole coupled ferromagnets, high or low temperature superconductors, and so on). Therefore, quantum topological order (QTO) can be described as a pattern of long-range quantum entanglement in quantum states, and it can be classified as an extended quantum symmetry in terms of categorical representations, categorical groups, locally compact quantum groupoid representations, braided tensor categories/ categories, quantum algebroids or quantum double groupoid representations.
Topological order theories and topological quantum computation were also recently reported to be of interest for the design of quantum computers [15], and thus such fundamental topological order theories might conceivably lead to practical applications in developing ultra-fast quantum supercomputers. A related concept is that of “quantum glassiness” [20] which incorporates many concepts from topological order theories.
- 1
- Levin M. and Wen X-G., Colloquium: Photons and electrons as emergent phenomena, Rev. Mod. Phys. 77, Nu 12:19, 9 April 2009 (UTC)871 (2005), 4 pages; also, Quantum ether: Photons and electrons from a rotor model.,
 . .
- 2
- Yetter D.N., TQFTs from homotopy 2-types., J. Knot Theory 2 (1993), 113–123.
- 3
- E. Witten, Quantum field theory and the Jones polynomial. Comm. Math. Phys., 121, 351 (1989).
- 4
- Xiao-Gang Wen., Vacuum Degeneracy of Chiral Spin State in Compactified Spaces., Phys. Rev. B, 40, 7387 (1989).
- 5
- Xiao-Gang Wen.,Topological Orders in Rigid States, Int. J. Mod. Phys., B4, 239 (1990).
- 6
- Ground state degeneracy of the FQH states in presence of random potential and on high genus Riemann surfaces, Xiao–Gang Wen and Qian Niu, Phys. Rev. B41, 9377 (1990).
- 7
- Landsman N. P. and Ramazan B., Quantization of Poisson algebras associated to Lie algebroids, in Proc. Conf. on Groupoids in Physics, Analysis and Geometry(Boulder CO, 1999), Editors J. Kaminker et al.,159–192 Contemp. Math. 282, Amer. Math. Soc., Providence RI, 2001,(also math–ph/001005.)
- 8
- Baianu, I.C. Non-Abelian Quantum Algebraic Topology (NAQAT) 20 Nov. (2008), 87 pages.
- 9
- Levin A. and Olshanetsky M., Hamiltonian Algebroids and deformations of complex structures on Riemann curves, hep–th/0301078v1.
- 10
- Levin M. and Wen X-G., Fermions, strings, and gauge fields in lattice spin models., Phys. Rev. B 67, 245316, (2003), 4 pages.
- 11
- Levin M. and Wen X-G., Detecting topological order in a ground state wave function., Phys. Rev. Letts.,96(11), 110405, (2006).
- 12
- Xiao-Gang Wen, Yong-Shi Wu and Y. Hatsugai., Chiral operator product algebra and edge excitations of a FQH droplet (pdf),Nucl. Phys. B422, 476 (1994): Used chiral operator product algebra to construct the bulk wave function, characterize the topological orders and calculate the edge states for some non-Abelian FQH states.
- 13
- Xiao-Gang Wen and Yong-Shi Wu., Chiral operator product algebra hidden in certain FQH states (pdf),Nucl. Phys. B419, 455 (1994): Demonstrated that non-Abelian topological orders are closely related to chiral operator product algebra (instead of conformal field theory).
- 14
- The concept:Non-Abelian theory.
- 15
- Algebraic Topology Foundations of Supersymmetry and Symmetry Breaking in Quantum Field Theory and Quantum Gravity: A Review., Baianu,I.C, Glazebrook, J. F., and Brown, R. In: Symmetry, Integrability and Geometry: Methods and Applications: SIGMA, (2009), 76 pages.
- 16
- R. Brown et al. A Non-Abelian, Categorical Ontology of Spacetimes and Quantum Gravity., Axiomathes, Volume 17, Numbers 3-4 / December, (2007), pages 353–408.,Springer,Netherlands,ISSN 1122-1151 (Print) 1572-8390 (Online). doi:10.1007/s10516-007-9012-1.
- 17
- Ronald Brown, Higgins, P. J. and R. Sivera,:(2009), Nonabelian Algebraic Topology., vols.1 and 2, Ch.U. Press, in press.
- 18
- A Bibliography for Categories and Algebraic Topology Applications in Theoretical Physics Quantum Algebraic Topology (QAT)
- 19
- Wen X-G., Quantum Field Theory of Many Body Systems–From the Origin of Sound to an Origin of Light and Electrons, Oxford Univ. Press, Oxford, 2004.
- 20
- Chamon, C., Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 040402 (2005),4 pages., Quantum Glassiness in Strongly Correlated Clean Systems: An Example of Topological Overprotection.
- 21
- Steve Weinberg., Quantum Theory of Fields., vol.3., Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK.
|
"Quantum topological order and extended quantum symmetries" is owned by bci1.
|
|
See Also: quantum symmetry
| Also defines: |
quantum topological order, glassiness, glass, metallic glass, quantum computers, quantum supercomputers, topological quantum computers, algebraic-topological computers, Fermi statistics, T_c, superconductivity, Coper pairs (of phonon-coupled electrons), many-body system, Cooper pairs, phonons, long-range correlations, quantum coherence, strongly correlated clean systems, quantum phase transition, Goldstone bosons, Goldstone theorem, high temperature superconductors, quantum algebroid, quantum double groupoid, quantum double groupoid representations, Anderson localization, delocalized quantum states, edge quantum states, QTO, QES, topological order, spontaneous symmetry breaking, Mott-Anderson transition, Mott-Hubbard transition, glass-transition, Landau symmetry-breaking, long-range coupling, quantum extended symmetry, phonons, quantum glassiness |
| Keywords: |
topology, order, topolgical order, symmetry, quantum topological order |
Cross-references: computation, topological, categories, tensor, groups, low temperature superconductors, concept, QG, quantum gravity, QFT, quantum field theories, extended quantum symmetry, solids, work, topological structures, algebraic, temperature, representations, locally compact quantum groupoid, quantum operator algebras, Quantum Algebraic Topology, systems
There are 30 references to this object.
This is version 25 of Quantum topological order and extended quantum symmetries, born on 2009-04-11, modified 2009-04-17.
Object id is 638, canonical name is QuantumTopologicalOrder.
Accessed 17999 times total.
Classification:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pending Errata and Addenda
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

