|
axiomatics and categorical foundations of mathematical physics
|
(Topic)
|
|
This is a contributed new topic on the mathematical foundations of theoretical physics and quantum theories.
- Axiomatic foundations of quantum field theories
- quantum logics and logic algebras: Post and
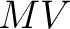 logics logics
- Index of Quantum Algebraic Topology
- adjointness, equivalence, isomorphism at the foundations of categorical physics
- category theory in quantum physics and general relativity
- Categories of quantum logic algebras
- functor categories and super-categories
- index of category theory
- indexes of category
- classification of
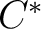 -algebras and groupoid convolution -algebras and groupoid convolution 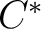 -algebras -algebras
- Quantum topoi and quantum logic extended-toposes
- non-Abelian structures and gauge theories
- Non-Abelian Quantum Algebraic Topology and AQFT
- Classical and categorical Galois theories of quantum groups and quantum groupoids
- Theory of quantum computation: quantum logics, quantum automata and quantum computation
- Measure theory and probability in quantum statistical mechanics
- quantum symmetries and quantum groupoid representation theory
- noncommutative geometry, SUSY and axiomatic quantum gravity (AQG)
Literature references for mathematical physics foundations: axiomatics and categories
- 1
- Alfsen, E.M. and F. W. Schultz: Geometry of State Spaces of Operator Algebras, Birkh'́auser, Boston–Basel–Berlin (2003).
- 2
- Atiyah, M.F. 1956. On the Krull-Schmidt theorem with applications to sheaves. Bull. Soc. Math. France, 84: 307–317.
- 3
- Awodey, S. & Butz, C., 2000, Topological Completeness for Higher Order Logic., Journal of Symbolic Logic, 65, 3, 1168–1182.
- 4
- Awodey, S., 1996, Structure in Mathematics and Logic: A Categorical Perspective, Philosophia Mathematica, 3: 209–237.
- 5
- Awodey, S., 2004, An Answer to Hellman's Question: Does Category Theory Provide a Framework for Mathematical Structuralism, Philosophia Mathematica, 12: 54–64.
- 6
- Awodey, S., 2006, Category Theory, Oxford: Clarendon Press.
- 7
- Baez, J. & Dolan, J., 1998a, Higher-Dimensional Algebra III. n-Categories and the Algebra of Opetopes, in: Advances in Mathematics, 135, 145–206.
- 8
- Baez, J. & Dolan, J., 1998b, “Categorification”, Higher Category Theory, Contemporary Mathematics, 230, Providence: AMS, 1–36.
- 9
- Baez, J. & Dolan, J., 2001, From Finite Sets to Feynman Diagrams, in Mathematics Unlimited – 2001 and Beyond, Berlin: Springer, 29–50.
- 10
- Baez, J., 1997, An Introduction to n-Categories, in Category Theory and Computer Science, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 1290, Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 1–33.
- 11
- Baianu, I.C.: 1971a, Organismic Supercategories and Qualitative Dynamics of Systems. Ibid., 33 (3), 339–354.
- 11
- Baianu, I.C.: 1971b, Categories, Functors and Quantum Algebraic Computations, in P. Suppes (ed.), Proceed. Fourth Intl. Congress Logic-Mathematics-Philosophy of Science, September 1–4, 1971, Bucharest.
- 12
- Baianu, I.C.: 2004a, Quantum Nano–Automata (QNA): Microphysical Measurements with Microphysical QNA Instruments, CERN Preprint EXT–2004–125.
- 13
- Baianu I. C., Brown R., Georgescu G. and J. F. Glazebrook: 2006b, Complex Nonlinear Biodynamics in Categories, Higher Dimensional Algebra and Łukasiewicz–Moisil Topos: Transformations of Neuronal, Genetic and Neoplastic Networks., Axiomathes, 16 Nos. 1–2: 65–122.
- 14
- Baianu, I.C., R. Brown and J. F. Glazebrook: 2007b, A Non-Abelian, Categorical Ontology of Spacetimes and Quantum Gravity, Axiomathes, 17: 169-225.
- 15
- Barr, M and C. Wells. Toposes, Triples and Theories. Montreal: McGill University, 2000.
- 16
- Barr, M. & Wells, C., 1999, Category Theory for Computing Science, Montreal: CRM.
- 17
- Batanin, M., 1998, Monoidal Globular Categories as a Natural Environment for the Theory of Weak n-Categories, Advances in Mathematics, 136: 39–103.
- 18
- Bell, J. L., 1981, Category Theory and the Foundations of Mathematics, British Journal for the Philosophy of Science, 32, 349–358.
- 19
- Bell, J. L., 1982, Categories, Toposes and Sets, Synthese, 51, 3, 293–337.
- 20
- Bell, J. L., 1986, From Absolute to Local Mathematics, Synthese, 69, 3, 409–426.
- 21
- Bell, J. L., 1988, Toposes and Local Set Theories: An Introduction, Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- 22
- Birkoff, G. & Mac Lane, S., 1999, Algebra, 3rd ed., Providence: AMS.
- 23
- Biss, D.K., 2003, Which Functor is the Projective Line?, American Mathematical Monthly, 110, 7, 574–592.
- 24
- Blass, A. & Scedrov, A., 1983, Classifying Topoi and Finite Forcing , Journal of Pure and Applied Algebra, 28, 111–140.
- 25
- Blass, A., 1984, The Interaction Between Category Theory and Set Theory., Mathematical Applications of Category Theory, 30, Providence: AMS, 5–29.
- 26
- Borceux, F.: 1994, Handbook of Categorical Algebra, vols: 1–3, in Encyclopedia of Mathematics and its Applications 50 to 52, Cambridge University Press.
- 27
- Bourbaki, N. 1961 and 1964: Algèbre commutative., in Èléments de Mathématique., Chs. 1–6., Hermann: Paris.
- 28
- R. Brown: Topology and Groupoids, BookSurge LLC (2006).
- 29
- Brown, R. and G. Janelidze: 2004, Galois theory and a new homotopy double groupoid of a map of spaces, Applied Categorical Structures 12: 63-80.
- 30
- Brown, R., Higgins, P. J. and R. Sivera,: 2007a, Non-Abelian Algebraic Topology, (vol. 2 in preparation; vol. 1 is available at Bangor Univ. R. Brown's website for download as PDF.)
- 31
- Brown, R., Glazebrook, J. F. and I.C. Baianu.: 2007b, A Conceptual, Categorical and Higher Dimensional Algebra Framework of Universal Ontology and the Theory of Levels for Highly Complex Structures and Dynamics., Axiomathes (17): 321–379.
- 32
- Brown, R., Hardie, K., Kamps, H. and T. Porter: 2002, The homotopy double groupoid of a Hausdorff space., Theory and Applications of Categories 10, 71-93.
- 33
- Brown, R., and Hardy, J.P.L.:1976, Topological groupoids I: universal constructions, Math. Nachr., 71: 273-286.
- 34
- Brown, R. and Spencer, C.B.: 1976, Double groupoids and crossed modules, Cah. Top. Géom. Diff. 17, 343-362.
- 35
- Brown R, and Porter T (2006) Category theory: an abstract setting for analogy and comparison. In: What is category theory? Advanced studies in mathematics and logic. Polimetrica Publisher, Italy, pp. 257-274.
- 36
- Brown R, Razak Salleh A (1999) Free crossed resolutions of groups and presentations of modules of identities among relations. LMS J. Comput. Math., 2: 25–61.
- 37
- Buchsbaum, D. A.: 1955, Exact categories and duality., Trans. Amer. Math. Soc. 80: 1-34.
- 38
- Bucur, I., and Deleanu A. (1968). Introduction to the Theory of Categories and Functors. J.Wiley and Sons: London
- 39
- Bunge, M. and S. Lack: 2003, Van Kampen theorems for toposes, Adv. in Math. 179, 291-317.
- 40
- Bunge, M., 1974, Topos Theory and Souslin's Hypothesis, Journal of Pure and Applied Algebra, 4, 159-187.
- 41
- Bunge, M., 1984, Toposes in Logic and Logic in Toposes, Topoi, 3, no. 1, 13-22.
- 42
- Bunge M, Lack S (2003) Van Kampen theorems for toposes. Adv Math, 179: 291-317.
- 43
- Butterfield J., Isham C.J. (2001) Spacetime and the philosophical challenges of quantum gravity. In: Callender C, Hugget N (eds) Physics meets philosophy at the Planck scale. Cambridge University Press, pp 33-89.
- 44
- Butterfield J., Isham C.J. 1998, 1999, 2000-2002, A topos perspective on the Kochen-Specker theorem I-IV, Int J Theor Phys 37(11):2669-2733; 38(3):827-859; 39(6):1413-1436; 41(4): 613-639.
- 45
- Cartan, H. and Eilenberg, S. 1956. Homological Algebra, Princeton Univ. Press: Pinceton.
- 46
- M. Chaician and A. Demichev. 1996. Introduction to Quantum Groups, World Scientific .
- 47
- Chevalley, C. 1946. The theory of Lie groups. Princeton University Press, Princeton NJ
- 48
- Cohen, P.M. 1965. Universal Algebra, Harper and Row: New York, london and Tokyo.
- 49
- M. Crainic and R. Fernandes.2003. Integrability of Lie brackets, Ann.of Math. 157: 575-620.
- 50
- Connes A 1994. Noncommutative geometry. Academic Press: New York.
- 51
- Croisot, R. and Lesieur, L. 1963. Algèbre noethérienne non-commutative., Gauthier-Villard: Paris.
- 52
- Crole, R.L., 1994, Categories for Types, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- 53
- Dieudonné, J. & Grothendieck, A., 1960, [1971], Éléments de Géométrie Algébrique, Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
- 54
- Dirac, P. A. M., 1930, The Principles of Quantum Mechanics, Oxford: Clarendon Press.
- 55
- Dirac, P. A. M., 1933, The Lagrangian in Quantum Mechanics, Physikalische Zeitschrift der Sowietunion, 3: 64-72.
- 56
- Dirac, P. A. M.,, 1943, Quantum Electrodynamics, Communications of the Dublin Institute for Advanced Studies, A1: 1-36.
- 57
- Dixmier, J., 1981, Von Neumann Algebras, Amsterdam: North-Holland Publishing Company. [First published in French in 1957: Les Algebres d'Operateurs dans l'Espace Hilbertien, Paris: Gauthier–Villars.]
- 58
- M. Durdevich : Geometry of quantum principal bundles I, Commun. Math. Phys. 175 (3) (1996), 457–521.
- 59
- M. Durdevich : Geometry of quantum principal bundles II, Rev. Math. Phys. 9 (5) (1997), 531–607.
- 60
- Ehresmann, C.: 1965, Catégories et Structures, Dunod, Paris.
- 60
- Ehresmann, C.: 1966, Trends Toward Unity in Mathematics., Cahiers de Topologie et Geometrie Differentielle 8: 1-7.
- 61
- Ehresmann, C.: 1952, Structures locales et structures infinitésimales, C.R.A.S. Paris 274: 587-589.
- 62
- Ehresmann, C.: 1959, Catégories topologiques et catégories différentiables, Coll. Géom. Diff. Glob. Bruxelles, pp.137-150.
- 63
- Ehresmann, C.:1963, Catégories doubles des quintettes: applications covariantes , C.R.A.S. Paris, 256: 1891–1894.
- 64
- Ehresmann, C.: 1984, Oeuvres complètes et commentées: Amiens, 1980-84, edited and commented by Andrée Ehresmann.
- 65
- Eilenberg, S. and S. Mac Lane.: 1942, Natural Isomorphisms in Group Theory., American Mathematical Society 43: 757-831.
- 66
- Eilenberg, S. and S. Mac Lane: 1945, The General Theory of Natural Equivalences, Transactions of the American Mathematical Society 58: 231-294.
- 67
- Eilenberg, S. & MacLane, S., 1942, Group Extensions and Homology, Annals of Mathematics, 43, 757–831.
- 68
- Eilenberg, S. & Steenrod, N., 1952, Foundations of Algebraic Topology, Princeton: Princeton University Press.
- 69
- Eilenberg, S.: 1960. Abstract description of some basic functors., J. Indian Math.Soc., 24 :221-234.
- 70
- S.Eilenberg. Relations between Homology and Homotopy Groups. Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.USA (1966),v:10–14.
- 71
- Ellerman, D., 1988, Category Theory and Concrete Universals, Synthese, 28, 409–429.
- 72
- Z. F. Ezawa, G. Tsitsishvilli and K. Hasebe : Noncommutative geometry, extended
 algebra and Grassmannian solitons in multicomponent Hall systems, arXiv:hep–th/0209198. algebra and Grassmannian solitons in multicomponent Hall systems, arXiv:hep–th/0209198.
- 73
- Fell, J. M. G., 1960. The Dual Spaces of C*-Algebras, Transactions of the American Mathematical Society, 94: 365-403.
- 74
- Feynman, R. P., 1948, Space–Time Approach to Non–Relativistic Quantum Mechanics., Reviews of Modern Physics, 20: 367–387. [It is reprinted in (Schwinger 1958).]
- 75
- Freyd, P., 1960. Functor Theory (Dissertation). Princeton University, Princeton, New Jersey.
- 76
- Freyd, P., 1963, Relative homological algebra made absolute. , Proc. Natl. Acad. USA, 49:19-20.
- 77
- Freyd, P., 1964, Abelian Categories. An Introduction to the Theory of Functors, New York and London: Harper and Row.
- 78
- Freyd, P., 1965, The Theories of Functors and Models., Theories of Models, Amsterdam: North Holland, 107–120.
- 79
- Freyd, P., 1966, Algebra-valued Functors in general categories and tensor product in particular., Colloq. Mat. 14: 89–105.
- 80
- Freyd, P., 1972, Aspects of Topoi,Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society, 7: 1–76.
- 81
- Freyd, P., 1990, Categories, Allegories, Amsterdam: North Holland.
- 82
- Freyd, P., 2002, “Cartesian Logic”, Theoretical Computer Science, 278, no. 1–2, 3–21.
- 83
- Freyd, P., Friedman, H. & Scedrov, A., 1987, “Lindembaum Algebras of Intuitionistic Theories and Free Categories”., Annals of Pure and Applied Logic, 35, 2, 167–172.
- 84
- Gablot, R. 1971. Sur deux classes de catégories de Grothendieck. Thesis.. Univ. de Lille.
- 85
- Gabriel, P.: 1962, Des catégories abéliennes, Bull. Soc. Math. France 90: 323-448.
- 86
- Gabriel, P. and M.Zisman:. 1967: Category of fractions and homotopy theory, Ergebnesse der math. Springer: Berlin.
- 87
- Gabriel, P. and N. Popescu: 1964, Caractérisation des catégories abéliennes avec générateurs et limites inductives. , CRAS Paris 258: 4188-4191.
- 88
- Galli, A. & Reyes, G. & Sagastume, M., 2000, Completeness Theorems via the Double Dual Functor, Studia Logical, 64, no. 1, 61–81.
- 89
- Gelfan'd, I. and Naimark, M., 1943. On the Imbedding of Normed Rings into the Ring of Operators in Hilbert Space., Recueil Mathématique [Matematicheskii Sbornik] Nouvelle Série, 12 [54]: 197-213. [Reprinted in C*–algebras: 1943–1993, in the series Contemporary Mathematics, 167, Providence, R.I. : American Mathematical Society, 1994.]
- 90
- Georgescu, G. and C. Vraciu 1970. “On the Characterization of Łukasiewicz Algebras.” J Algebra, 16 (4), 486-495.
- 91
- Ghilardi, S. & Zawadowski, M., 2002, Sheaves, Games & Model Completions: A Categorical Approach to Nonclassical Porpositional Logics, Dordrecht: Kluwer.
- 92
- Ghilardi, S., 1989, Presheaf Semantics and Independence Results for some Non-classical first-order logics, Archive for Mathematical Logic, 29, no. 2, 125–136.
- 93
- Goblot, R., 1968, Catégories modulaires , C. R. Acad. Sci. Paris, Série A., 267: 381–383.
- 94
- Goblot, R., 1971, Sur deux classes de catégories de Grothendieck, Thèse., Univ. Lille, 1971.
- 95
- Goldblatt, R., 1979, Topoi: The Categorical Analysis of Logic, Studies in logic and the foundations of mathematics, Amsterdam: Elsevier North-Holland Publ. Comp.
- 96
- Goldie, A. W., 1964, Localization in non-commutative noetherian rings, J.Algebra, 1: 286-297.
- 97
- Godement,R. 1958. Théorie des faisceaux. Hermann: Paris.
- 98
- Gray, C. W.: 1965. Sheaves with values in a category.,Topology, 3: 1-18.
- 99
- Grothendieck, A.: 1971, Revêtements Étales et Groupe Fondamental (SGA1), chapter VI: Catégories fibrées et descente, Lecture Notes in Math. 224, Springer–Verlag: Berlin.
- 100
- Grothendieck, A.: 1957, Sur quelque point d-algébre homologique. , Tohoku Math. J., 9: 119-121.
- 101
- Grothendieck, A. and J. Dieudoné.: 1960, Eléments de geometrie algébrique., Publ. Inst. des Hautes Etudes de Science, 4.
- 102
- Grothendieck, A. et al., Séminaire de Géométrie Algébrique, Vol. 1–7, Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
- 103
- Groups Authors: J. Faria Martins, Timothy Porter., On Yetter's Invariant and an Extension of the Dijkgraaf-Witten Invariant to Categorical
![$math.QA/0608484 [abs, ps, pdf, other]$ $math.QA/0608484 [abs, ps, pdf, other]$](http://images.physicslibrary.org/cache/objects/477/l2h/img5.png) . .
- 104
- Gruson, L, 1966, Complétion abélienne. Bull. Math.Soc. France, 90: 17-40.
- 105
- K.A. Hardie, K.H. Kamps and R.W. Kieboom. 2000. A homotopy 2-groupoid of a Hausdorff space, Applied Cat. Structures 8: 209–234.
- 106
- Hatcher, W. S. 1982. The Logical Foundations of Mathematics, Oxford: Pergamon Press.
- 107
- Heller, A. :1958, Homological algebra in Abelian categories., Ann. of Math. 68: 484-525.
- 108
- Heller, A. and K. A. Rowe.:1962, On the category of sheaves., Amer J. Math. 84: 205-216.
- 109
- Hermida, C. & Makkai, M. & Power, J., 2000, On Weak Higher-dimensional Categories. I, Journal of Pure and Applied Algebra, 154, no. 1-3, 221–246.
- 110
- Hermida, C. & Makkai, M. & Power, J., 2001, On Weak Higher-dimensional Categories. II, Journal of Pure and Applied Algebra, 157, no. 2-3, 247–277.
- 111
- Hermida, C. & Makkai, M. & Power, J., 2002, On Weak Higher-dimensional Categories. III, Journal of Pure and Applied Algebra, 166, no. 1-2, 83–104.
- 112
- Higgins, P. J.: 2005, Categories and groupoids, Van Nostrand Mathematical Studies: 32, (1971); Reprints in Theory and Applications of Categories, No. 7: 1-195.
- 113
- Higgins, Philip J. Thin elements and commutative shells in cubical
 -categories. Theory Appl. Categ. 14 (2005), No. 4, 60–74 (electronic). msc: 18D05. -categories. Theory Appl. Categ. 14 (2005), No. 4, 60–74 (electronic). msc: 18D05.
- 114
- Hyland, J.M.E. & Robinson, E.P. & Rosolini, G., 1990, The Discrete Objects in the Effective Topos, Proceedings of the London Mathematical Society (3), 60, no. 1, 1–36.
- 115
- Hyland, J. M..E., 1988, A Small Complete Category, Annals of Pure and Applied Logic, 40, no. 2, 135–165.
- 116
- Hyland, J. M .E., 1991, First Steps in Synthetic Domain Theory, Category Theory (Como 1990), Lecture Notes in Mathematics, 1488, Berlin: Springer, 131-156.
- 117
- Hyland, J. M.E., 2002, Proof Theory in the Abstract, Annals of Pure and Applied Logic, 114, no. 1–3, 43–78.
- 118
- E.Hurewicz. CW Complexes.Trans AMS.1955.
- 119
- Ionescu, Th., R. Parvan and I. Baianu, 1970, C. R. Acad. Sci. Paris, Série A., 269: 112-116, communiquée par Louis Néel.
- 120
- C. J. Isham : A new approach to quantising space–time: I. quantising on a general category, Adv. Theor. Math. Phys. 7 (2003), 331–367.
- 121
- Jacobs, B., 1999, Categorical Logic and Type Theory, Amsterdam: North Holland.
- 122
- Johnstone, P. T., 1977, Topos Theory, New York: Academic Press.
- 123
- Johnstone, P. T., 1979a, Conditions Related to De Morgan's Law, Applications of Sheaves, Lecture Notes in Mathematics, 753, Berlin: Springer, 479–491.
- 124
- Johnstone, P. T., 1982, Stone Spaces, Cambridge:Cambridge University Press.
- 125
- Johnstone, P. T., 1985, “How General is a Generalized Space?”, Aspects of Topology, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 77–111.
- 126
- Joyal, A. & Moerdijk, I., 1995, Algebraic Set Theory, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- 127
- Van Kampen, E. H.: 1933, On the Connection Between the Fundamental Groups of some Related Spaces, Amer. J. Math. 55: 261-267
- 128
- Kan, D. M., 1958, Adjoint Functors, Transactions of the American Mathematical Society, 87, 294-329.
- 129
- Kleisli, H.: 1962, Homotopy theory in Abelian categories.,Can. J. Math., 14: 139-169.
- 130
- Knight, J.T., 1970, On epimorphisms of non-commutative rings., Proc. Cambridge Phil. Soc., 25: 266-271.
- 131
- Kock, A., 1981, Synthetic Differential Geometry, London Mathematical Society Lecture Note Series, 51, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- 132
- S. Kobayashi and K. Nomizu. Foundations of Differential Geometry Vol I., Wiley Interscience, New York–London 1963.
- 133
- H. Krips.1999. Measurement in Quantum Theory., The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Winter 1999 Edition), Edward N. Zalta (ed.)
- 134
- Lam, T. Y., 1966, “The category of noetherian modules.”, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 55: 1038-104.
- 135
- Lambek, J. & Scott, P. J., 1981, Intuitionistic Type Theory and Foundations, Journal of Philosophical Logic, 10, 1, 101–115.
- 136
- Lambek, J., 1968, Deductive Systems and Categories I. Syntactic Calculus and Residuated Categories, Mathematical Systems Theory, 2, 287–318.
- 137
- Lambek, J., 1969, Deductive Systems and Categories II. Standard Constructions and Closed Categories, Category Theory, Homology Theory and their Applications I, Berlin: Springer, 76–122.
- 138
- Lambek, J., 1972, Deductive Systems and Categories III. Cartesian Closed Categories, Intuitionistic Propositional Calculus, and Combinatory Logic, Toposes, Algebraic Geometry and Logic, Lecture Notes in Mathematics, 274, Berlin: Springer, 57–82.
- 139
- Lambek, J., 1989A, On Some Connections Between Logic and Category Theory, Studia Logica, 48, 3, 269–278.
- 140
- Lambek, J., 1989B, On the Sheaf of Possible Worlds, Categorical Topology and its relation to Analysis, Algebra and Combinatorics, Teaneck: World Scientific Publishing, 36–53.
- 141
- Lambek, J., 1994a, Some Aspects of Categorical Logic, in Logic, Methodology and Philosophy of Science IX, Studies in Logic and the Foundations of Mathematics 134, Amsterdam: North Holland, 69–89.
- 142
- Lambek, J., 1994b, What is a Deductive System?, What is a Logical System?, Studies in Logic and Computation, 4, Oxford: Oxford University Press, 141–159.
- 143
- Lambek, J., 2004, What is the world of Mathematics? Provinces of Logic Determined, Annals of Pure and Applied Logic, 126(1-3), 149–158.
- 144
- Lambek, J. and P. J. Scott. Introduction to higher order categorical logic. Cambridge University Press, 1986.
- 145
- E. C. Lance : Hilbert C*–Modules. London Math. Soc. Lect. Notes 210, Cambridge Univ. Press. 1995.
- 146
- Landry, E. & Marquis, J.-P., 2005, Categories in Context: Historical, Foundational and philosophical, Philosophia Mathematica, 13, 1–43.
- 147
- Landry, E., 2001, Logicism, Structuralism and Objectivity, Topoi, 20, 1, 79–95.
- 148
- Landsman, N. P.: 1998, Mathematical Topics between Classical and Quantum Mechanics, Springer Verlag: New York.
- 149
- N. P. Landsman : Mathematical topics between classical and quantum mechanics. Springer Verlag, New York, 1998.
- 150
- N. P. Landsman : Compact quantum groupoids,
- 151
- La Palme Reyes, M., et. al., 1994, The non-Boolean Logic of Natural Language Negation, Philosophia Mathematica, 2, no. 1, 45–68.
- 152
- La Palme Reyes, M., et. al., 1999, Count Nouns, Mass Nouns, and their Transformations: a Unified Category-theoretic Semantics, in Language, Logic and Concepts, Cambridge: MIT Press, 427–452.
- 153
- Lawvere, F. W., 1964, An Elementary Theory of the Category of Sets, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences U.S.A., 52, 1506–1511.
- 154
- Lawvere, F. W., 1965, Algebraic Theories, Algebraic Categories, and Algebraic Functors, in Theory of Models, Amsterdam: North Holland, 413–418.
- 155
- Lawvere, F. W., 1966, The Category of Categories as a Foundation for Mathematics, in Proceedings of the Conference on Categorical Algebra, La Jolla, New York: Springer-Verlag, 1–21.
- 156
- Lawvere, F. W., 1969a, Diagonal Arguments and Cartesian Closed Categories, in Category Theory, Homology Theory, and their Applications II, Berlin: Springer, 134–145.
- 157
- Lawvere, F. W., 1969b, Adjointness in Foundations, Dialectica, 23, 281–295.
- 158
- Lawvere, F. W., 1970, Equality in Hyper-doctrines and Comprehension Schema as an Adjoint Functor, Applications of Categorical Algebra, Providence: AMS, 1-14.
- 159
- Lawvere, F. W., 1971, Quantifiers and Sheaves, Actes du CongrÉs International des MathÉmaticiens, Tome 1, Paris: Gauthier-Villars, 329–334.
- 160
- Lawvere, F. W., 1972, “Introduction”, in Toposes, Algebraic Geometry and Logic, Lecture Notes in Mathematics, 274, Springer-Verlag, 1–12.
- 161
- Lawvere, F. W., 1975, Continuously Variable Sets: Algebraic Geometry = Geometric Logic, in Proceedings of the Logic Colloquium Bristol 1973, Amsterdam: North Holland, 135–153.
- 162
- Lawvere, F. W., 1976, Variable Quantities and Variable Structures in Topoi, in Algebra, Topology, and Category Theory, New York: Academic Press, 101–131.
- 163
- Lawvere, F. W.: 1963, Functorial Semantics of Algebraic Theories, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, Mathematics, 50: 869-872.
- 164
- Lawvere, F. W.: 1969, Closed Cartesian Categories., Lecture held as a guest of the Romanian Academy of Sciences, Bucharest.
- 165
- Lawvere, F. W., 1992. Categories of Space and of Quantity, The Space of Mathematics, Foundations of Communication and Cognition.
- 166
- Lawvere, F. W., 2002, Categorical Algebra for Continuum Micro-Physics, Journal of Pure and Applied Algebra, 175, no. 1–3, 267–287.
- 167
- Lawvere, F. W., 2003, Foundations and Applications: Axiomatization and Education. New Programs and Open Problems in the Foundation of Mathematics, Bulletin of Symbolic Logic, 9, 2, 213–224.
- 168
- Leinster, T., 2002, A Survey of Definitions of n-categories, in Theory and Applications of Categories, (electronic), 10, 1–70.
- 169
- Li, M. and P. Vitanyi: 1997, An introduction to Kolmogorov Complexity and its Applications, Springer Verlag: New York.
- 170
- Lubkin, S., 1960. Imbedding of abelian categories., Trans. Amer. Math. Soc., 97: 410-417.
- 171
- K. C. H. Mackenzie : Lie Groupoids and Lie Algebroids in Differential Geometry, LMS Lect. Notes 124, Cambridge University Press, 1987
- 172
- MacLane, S.: 1948. Groups, categories, and duality., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci.U.S.A, 34: 263-267.
- 173
- MacLane, S., 1969, Foundations for Categories and Sets, in Category Theory, Homology Theory and their Applications II, Berlin: Springer, 146–164.
- 174
- MacLane, S., 1971, Categorical algebra and Set-Theoretic Foundations, in Axiomatic Set Theory, Providence: AMS, 231–240.
- 175
- Mac Lane, S., 1975, Sets, Topoi, and Internal Logic in Categories, in Studies in Logic and the Foundations of Mathematics, 80, Amsterdam: North Holland, 119-134.
- 176
- Mac Lane, S., 1981, Mathematical Models: a Sketch for the Philosophy of Mathematics, American Mathematical Monthly, 88, 7, 462–472.
- 177
- Mac Lane, S., 1986, Mathematics, Form and Function, New York: Springer.
- 178
- Mac Lane, S., 1988, Concepts and Categories in Perspective, in A Century of Mathematics in America, Part I, Providence: AMS, 323–365.
- 179
- Mac Lane, S., 1989, The Development of Mathematical Ideas by Collision: the Case of Categories and Topos Theory, in Categorical Topology and its Relation to Analysis, Algebra and Combinatorics, Teaneck: World Scientific, 1–9.
- 180
- MacLane, S., 1950, Dualities for Groups, Bulletin of the American Mathematical Society, 56, 485–516.
- 181
- Mac Lane, S., 1996, Structure in Mathematics. Mathematical Structuralism., Philosophia Mathematica, 4, 2, 174-183.
- 182
- Mac Lane, S., 1997, Categories for the Working Mathematician, 2nd edition, New York: Springer-Verlag.
- 183
- Mac Lane, S., 1997, Categorical Foundations of the Protean Character of Mathematics., Philosophy of Mathematics Today, Dordrecht: Kluwer, 117-122.
- 184
- Mac Lane, S., and I. Moerdijk. Sheaves and Geometry in Logic: A First Introduction to Topos Theory, Springer-Verlag, 1992.
- 185
- Majid, S.: 1995, Foundations of Quantum Group Theory, Cambridge Univ. Press: Cambridge, UK.
- 186
- Majid, S.: 2002, A Quantum Groups Primer, Cambridge Univ.Press: Cambridge, UK.
- 187
- Makkai, M. and Paré, R., 1989, Accessible Categories: the Foundations of Categorical Model Theory, Contemporary Mathematics 104, Providence: AMS.
- 188
- Makkai, M. and Reyes, G., 1977, First-Order Categorical Logic, Springer Lecture Notes in Mathematics 611, New York: Springer.
- 189
- Makkai, M., 1998, Towards a Categorical Foundation of Mathematics, in Lecture Notes in Logic, 11, Berlin: Springer, 153–190.
- 190
- Makkai, M., 1999, On Structuralism in Mathematics, in Language, Logic and Concepts, Cambridge: MIT Press, 43–66.
- 187
- Makkei, M. & Reyes, G., 1995, Completeness Results for Intuitionistic and Modal Logic in a Categorical Setting, Annals of Pure and Applied Logic, 72, 1, 25–101.
- 191
- Mallios, A. and I. Raptis: 2003, Finitary, Causal and Quantal Vacuum Einstein Gravity, Int. J. Theor. Phys. 42: 1479.
- 192
- Manders, K.L.: 1982, On the space-time ontology of physical theories, Philosophy of Science 49 no. 4: 575–590.
- 193
- Marquis, J.-P., 1993, Russell's Logicism and Categorical Logicisms, in Russell and Analytic Philosophy, A. D. Irvine & G. A. Wedekind, (eds.), Toronto, University of Toronto Press, 293–324.
- 194
- Marquis, J.-P., 1995, Category Theory and the Foundations of Mathematics: Philosophical Excavations., Synthese, 103, 421–447.
- 195
- Marquis, J.-P., 2000, Three Kinds of Universals in Mathematics?, in Logical Consequence: Rival Approaches and New Studies in Exact Philosophy: Logic, Mathematics and Science, Vol. II, B. Brown and J. Woods, eds., Oxford: Hermes, 191-212, 2000 ,
- 196
- Marquis, J.-P., 2006, Categories, Sets and the Nature of Mathematical Entities, in: The Age of Alternative Logics. Assessing philosophy of logic and mathematics today, J. van Benthem, G. Heinzmann, Ph. Nabonnand, M. Rebuschi, H.Visser, eds., Springer,181-192.
- 197
- Martins, J. F and T. Porter: 2004, On Yetter's Invariant and an Extension of the Dijkgraaf-Witten Invariant to Categorical Groups,
- 198
- May, J.P. 1999, A Concise Course in Algebraic Topology, The University of Chicago Press: Chicago.
- 199
- Mc Larty, C., 1991, Axiomatizing a Category of Categories, Journal of Symbolic Logic, 56, no. 4, 1243-1260.
- 200
- Mc Larty, C., 1992, Elementary Categories, Elementary Toposes, Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- 201
- Mc Larty, C., 1994, Category Theory in Real Time, Philosophia Mathematica, 2, no. 1, 36-44.
- 202
- Misra, B., I. Prigogine and M. Courbage.: 1979. Lyapounov variables: Entropy and measurement in quantum mechanics, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 78 (10): 4768-4772.
- 203
- Mitchell, B.: 1965, Theory of Categories, Academic Press:London.
- 204
- Mitchell, B.: 1964, The full imbedding theorem. Amer. J. Math. 86: 619-637.
- 205
- Moerdijk, I. & Palmgren, E., 2002, Type Theories, Toposes and Constructive Set Theory: Predicative Aspects of AST., Annals of Pure and Applied Logic, 114, no. 1–3, 155-201.
- 206
- Moerdijk, I., 1998, Sets, Topoi and Intuitionism., Philosophia Mathematica, 6, no. 2, 169-177.
- 207
- I. Moerdijk : Classifying toposes and foliations, Ann. Inst. Fourier, Grenoble 41, 1 (1991) 189-209.
- 208
- I. Moerdijk : Introduction to the language of stacks and gerbes, arXiv:math.AT/0212266 (2002).
- 209
- Morita, K. 1962. Category isomorphism and endomorphism rings of modules, Trans. Amer. Math. Soc., 103: 451-469.
- 210
- Morita, K. , 1970. Localization in categories of modules. I., Math. Z., 114: 121-144.
- 211
- M. A. Mostow : The differentiable space structure of Milnor classifying spaces, simplicial complexes, and geometric realizations, J. Diff. Geom. 14 (1979) 255-293.
- 212
- Oberst, U.: 1969, Duality theory for Grothendieck categories., Bull. Amer. Math. Soc. 75: 1401-1408.
- 213
- Oort, F.: 1970. On the definition of an abelian category. Proc. Roy. Neth. Acad. Sci. 70: 13-02.
- 214
- Ore, O., 1931, Linear equations on non-commutative fields, Ann. Math. 32: 463-477.
- 215
- Penrose, R.: 1994, Shadows of the Mind, Oxford University Press: Oxford.
- 216
- Plymen, R.J. and P. L. Robinson: 1994, Spinors in Hilbert Space, Cambridge Tracts in Math. 114, Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge.
- 217
- Pareigis, B., 1970, Categories and Functors, New York: Academic Press.
- 218
- Pedicchio, M. C. & Tholen, W., 2004, Categorical Foundations, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- 219
- Pitts, A. M., 2000, Categorical Logic, in Handbook of Logic in Computer Science, Vol.5, Oxford: Oxford Unversity Press, 39–128.
- 220
- Plotkin, B., 2000, Algebra, Categories and Databases, in Handbook of Algebra, Vol. 2, Amsterdam: Elsevier, 79–148.
- 221
- Popescu, N.: 1973, Abelian Categories with Applications to Rings and Modules. New York and London: Academic Press., 2nd edn. 1975. (English translation by I.C. Baianu).
- 222
- Pradines, J.: 1966, Théorie de Lie pour les groupoides différentiable, relation entre propriétes locales et globales, C. R. Acad Sci. Paris Sér. A 268: 907-910.
- 223
- Pribram, K. H.: 2000, Proposal for a quantum physical basis for selective learning, in (Farre, ed.) Proceedings ECHO IV 1-4.
- 224
- Prigogine, I.: 1980, From Being to Becoming : Time and Complexity in the Physical Sciences, W. H. Freeman and Co.: San Francisco.
- 225
- Raptis, I. and R. R. Zapatrin: 2000, Quantisation of discretized spacetimes and the correspondence principle, Int. Jour. Theor. Phys. 39: 1.
- 226
- Raptis, I.: 2003, Algebraic quantisation of causal sets, Int. Jour. Theor. Phys. 39: 1233.
- 227
- I. Raptis : Quantum space–time as a quantum causal set, arXiv:gr–qc/0201004.
- 228
- Reyes, G. and Zolfaghari, H., 1991, Topos-theoretic Approaches to Modality, Category Theory (Como 1990), Lecture Notes in Mathematics, 1488, Berlin: Springer, 359–378.
- 229
- Reyes, G. andZolfaghari, H., 1996, Bi-Heyting Algebras, Toposes and Modalities, Journal of Philosophical Logic, 25, no. 1, 25–43.
- 230
- Reyes, G., 1974, From Sheaves to Logic, in Studies in Algebraic Logic, A. Daigneault, ed., Providence: AMS.
- 231
- Reyes, G., 1991, A Topos-theoretic Approach to Reference and Modality., Notre Dame Journal of Formal Logic, 32, no. 3, 359-391.
- 232
- M. A. Rieffel : Group C*–algebras as compact quantum metric spaces, Documenta Math. 7 (2002), 605-651.
- 233
- Roberts, J. E.: 2004, More lectures on algebraic quantum field theory, in A. Connes, et al. Noncommutative Geometry, Springer: Berlin and New York.
- 234
- Rodabaugh, S. E. & Klement, E. P., eds., Topological and Algebraic Structures in Fuzzy Sets: A Handbook of Recent Developments in the Mathematics of Fuzzy Sets, Trends in Logic, 20, Dordrecht: Kluwer.
- 235
- Rota, G. C. : On the foundation of combinatorial theory, I. The theory of Möbius functions, Zetschrif für Wahrscheinlichkeitstheorie 2 (1968), 340.
- 236
- Rovelli, C.: 1998, Loop Quantum Gravity, in N. Dadhich, et al. Living Reviews in Relativity (refereed electronic journal)
- 237
- Schrödinger E.: 1945, What is Life?, Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK.
- 238
- Scott, P. J., 2000, Some Aspects of Categories in Computer Science, Handbook of Algebra, Vol. 2, Amsterdam: North Holland, 3–77.
- 239
- Seely, R. A. G., 1984, Locally Cartesian Closed Categories and Type Theory, Mathematical Proceedings of the Cambridge Mathematical Society, 95, no. 1, 33-48.
- 240
- Shapiro, S., 2005, Categories, Structures and the Frege-Hilbert Controversy: the Status of Metamathematics, Philosophia Mathematica, 13, 1, 61–77.
- 241
- Sorkin, R.D.: 1991, Finitary substitute for continuous topology, Int. J. Theor. Phys. 30 No. 7.: 923–947.
- 242
- Smolin, L.: 2001, Three Roads to Quantum Gravity, Basic Books: New York.
- 243
- Spanier, E. H.: 1966, Algebraic Topology, McGraw Hill: New York.
- 244
- Stapp, H.: 1993, Mind, Matter and Quantum Mechanics, Springer Verlag: Berlin–Heidelberg–New York.
- 245
- Stewart, I. and Golubitsky, M. : 1993. Fearful Symmetry: Is God a Geometer?, Blackwell: Oxford, UK.
- 246
- Szabo, R. J.: 2003, Quantum field theory on non-commutative spaces, Phys. Rep. 378: 207–209.
- 247
- Taylor, P., 1996, Intuitionistic sets and Ordinals, Journal of Symbolic Logic, 61 : 705-744.
- 248
- Taylor, P., 1999, Practical Foundations of Mathematics, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- 249
- Unruh, W.G.: 2001, Black holes, dumb holes, and entropy, in C. Callender and N. Hugget (eds. ) Physics Meets Philosophy at the Planck scale, Cambridge University Press, pp. 152-173.
- 250
- Van der Hoeven, G. and Moerdijk, I., 1984a, Sheaf Models for Choice Sequences, Annals of Pure and Applied Logic, 27, no. 1, 63–107.
- 251
- Várilly, J. C.: 1997, An introduction to noncommutative geometry
arXiv:physics/9709045 London.
- 252
- von Neumann, J.: 1932, Mathematische Grundlagen der Quantenmechanik, Springer: Berlin.
- 253
- Weinstein, A.: 1996, Groupoids : unifying internal and external symmetry, Notices of the Amer. Math. Soc. 43: 744–752.
- 254
- Wess J. and J. Bagger: 1983, Supersymmetry and Supergravity, Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ.
- 255
- Weinberg, S.: 1995, The Quantum Theory of Fields vols. 1 to 3, Cambridge Univ. Press.
- 256
- Wheeler, J. and W. Zurek: 1983, Quantum Theory and Measurement, Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ.
- 257
- Whitehead, J. H. C.: 1941, On adding relations to homotopy groups, Annals of Math. 42 (2): 409–428.
- 258
- Woit, P.: 2006, Not Even Wrong: The Failure of String Theory and the Search for Unity in Physical Laws, Jonathan Cape.
- 259
- Wood, R.J., 2004, Ordered Sets via Adjunctions, In: Categorical Foundations, M. C. Pedicchio & W. Tholen, eds., Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
|
"axiomatics and categorical foundations of mathematical physics" is owned by bci1.
|
|
Cross-references: quantum gravity, SUSY, noncommutative geometry, representation, quantum symmetries, quantum statistical mechanics, quantum automata, computation, quantum groupoids, quantum groups, AQFT, Non-Abelian Quantum Algebraic Topology, non-Abelian, convolution, groupoid, classification, indexes of category, index of category theory, super-categories, functor categories, general relativity, category theory, categorical physics, isomorphism, adjointness, Quantum Algebraic Topology, quantum logics, quantum field theories, quantum theories, theoretical physics
This is version 1 of axiomatics and categorical foundations of mathematical physics, born on 2009-02-03.
Object id is 477, canonical name is AxiomaticsAndCategoricalFoundationsOfMathematicalPhysics.
Accessed 966 times total.
Classification:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pending Errata and Addenda
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

