|
algebraic category of LMn -logic algebras
|
(Topic)
|
|
|
This is a topic entry on the algebraic category of Łukasiewicz–Moisil n-valued logic algebras that provides basic concepts and the background of the modern development in this area of many-valued logics.
The category
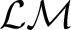 of Łukasiewicz-Moisil, of Łukasiewicz-Moisil, 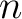 -valued logic algebras ( -valued logic algebras (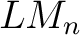 ), and ), and 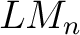 –lattice morphisms, –lattice morphisms,
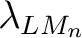 , was introduced in 1970 in ref. [1] as an algebraic category tool for , was introduced in 1970 in ref. [1] as an algebraic category tool for 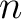 -valued logic studies. The objects of -valued logic studies. The objects of
 are the non–commutative are the non–commutative 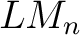 lattices and the morphisms of lattices and the morphisms of
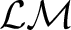 are the are the 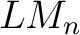 -lattice morphisms as defined here in the section following a brief historical note.
Łukasiewicz logic algebras were constructed by Grigore Moisil in 1941 to define `nuances' in logics, or many-valued logics, as well as 3-state control logic (electronic) circuits. Łukasiewicz-Moisil ( -lattice morphisms as defined here in the section following a brief historical note.
Łukasiewicz logic algebras were constructed by Grigore Moisil in 1941 to define `nuances' in logics, or many-valued logics, as well as 3-state control logic (electronic) circuits. Łukasiewicz-Moisil (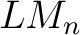 ) logic algebras were defined axiomatically in 1970, in ref. [1], as n-valued logic algebra representations and extensions of the Łukasiewcz (3-valued) logics; then, the universal properties of categories of ) logic algebras were defined axiomatically in 1970, in ref. [1], as n-valued logic algebra representations and extensions of the Łukasiewcz (3-valued) logics; then, the universal properties of categories of 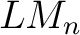 -logic algebras were also investigated and reported in a series of recent publications ([2] and references cited therein). Recently,
several modifications of -logic algebras were also investigated and reported in a series of recent publications ([2] and references cited therein). Recently,
several modifications of 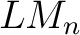 -logic algebras are under consideration as valid candidates for representations of quantum logics, as well as for modeling non-linear biodynamics in genetic `nets' or networks ([3]), and in single-cell organisms, or in tumor growth. For a recent review on -logic algebras are under consideration as valid candidates for representations of quantum logics, as well as for modeling non-linear biodynamics in genetic `nets' or networks ([3]), and in single-cell organisms, or in tumor growth. For a recent review on 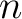 -valued logic algebras, and major published results, the reader is referred to [2]. -valued logic algebras, and major published results, the reader is referred to [2].
Definition 0.1 (reported by G. Moisil in 1941, cited in refs. [ 1, 2]).
A 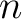 –valued Łukasiewicz–Moisil algebra, ( –valued Łukasiewicz–Moisil algebra, (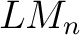 –algebra) is a structure of the form –algebra) is a structure of the form
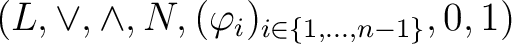 , subject to the following axioms: , subject to the following axioms:
Note that, for 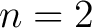 , ,
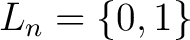 , and there is only one Chrysippian endomorphism of , and there is only one Chrysippian endomorphism of 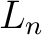 is is 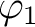 , which is necessarily restricted by the determination principle to a bijection, thus making , which is necessarily restricted by the determination principle to a bijection, thus making 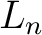 a Boolean algebra (if we were also to disregard the redundant bijection a Boolean algebra (if we were also to disregard the redundant bijection  ). Hence, the `overloaded' notation ). Hence, the `overloaded' notation  , which is used for both the classical Boolean algebra and the two–element
LM , which is used for both the classical Boolean algebra and the two–element
LM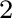 –algebra, remains consistent. –algebra, remains consistent.
- 1
- Georgescu, G. and C. Vraciu. 1970, On the characterization of centered Łukasiewicz algebras., J. Algebra, 16: 486-495.
- 2
- Georgescu, G. 2006, N-valued Logics and Łukasiewicz-Moisil Algebras, Axiomathes, 16 (1-2): 123-136.
- 3
- Baianu, I.C.: 1977, A Logical Model of Genetic Activities in Łukasiewicz Algebras: The Non-linear Theory. Bulletin of Mathematical Biology, 39: 249-258.
- 4
- Georgescu, G. and D. Popescu. 1968, On Algebraic Categories, Revue Roumaine de Mathématiques Pures et Appliquées, 13: 337-342.
Footnotes
-

- The
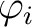 's are called the Chrysippian endomorphisms of 's are called the Chrysippian endomorphisms of 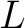 . .
|
"algebraic category of LMn -logic algebras" is owned by bci1.
|
|
See Also: categorical algebra, differential propositional calculus
| Other names: |
\Lukasiewicz-Moisil n-valued logic algebras, N-valued logic algebras, many-valued logic |
| Also defines: |
LMn -logic algebra,  -logic algebra, many-valued logic -logic algebra, many-valued logic |
| Keywords: |
algebraic category of LMn -logic algebras, genetic nets, Jan \L{}ukasiewicz, topic on algebra classification, axioms of metacategories and supercategories, non-Abelian theory, non-Abelian structures, non-commutative dynamic modeling diagrams, generalized toposes with many-valued logic subobject classifiers, quantum logics toposes, topic entry on foundations of mathematics, axiomatic theories and categorical foundations of mathematics-II, axiomatics and categorical foundations of mathematical physics, categorical algebra, topic on algebra classification, topic entry on the algebraic foundations of mathematics, Jordan-Banach and Jordan-Lie algebras, ETAS interpretation, examples of abelian categories, genetic nets, category theory |
Cross-references: operations, quantum logics, representations, section, morphisms, objects, category, algebraic category
There are 13 references to this object.
This is version 4 of algebraic category of LMn -logic algebras, born on 2009-01-31, modified 2009-05-16.
Object id is 460, canonical name is AlgebraicCategoryOfLMnLogicAlgebras.
Accessed 4767 times total.
Classification:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pending Errata and Addenda
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

