|
Grassmann-Hopf algebras and coalgebras\gebras
|
(Topic)
|
|
|
Let 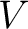 be a (complex) vector space, be a (complex) vector space,
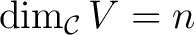 , and let , and let
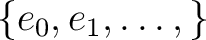 with identity with identity
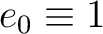 , be the generators of a Grassmann (exterior) algebra , be the generators of a Grassmann (exterior) algebra
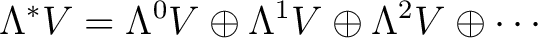 |
(0.1) |
subject to the relation
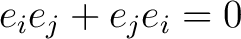 . Following Fauser (2004) we append this algebra with a Hopf structure to obtain a `co–gebra' based on the interchange (or `tangled duality'http://physicslibrary.org/encyclopedia/TrivialGroupoid.html): . Following Fauser (2004) we append this algebra with a Hopf structure to obtain a `co–gebra' based on the interchange (or `tangled duality'http://physicslibrary.org/encyclopedia/TrivialGroupoid.html):
( objects/points, morphisms)  ( morphisms, objects/points.) This leads to a tangle duality between an associative (unital algebra)
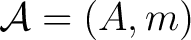 , and an associative (unital) `co–gebra' , and an associative (unital) `co–gebra'
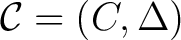 : :
, where the Sweedler notation (Sweedler, 1996), with respect to an arbitrary basis is adopted:
Here the
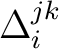 are called `section coefficients'. We have then a generalization of associativity to coassociativity: are called `section coefficients'. We have then a generalization of associativity to coassociativity:
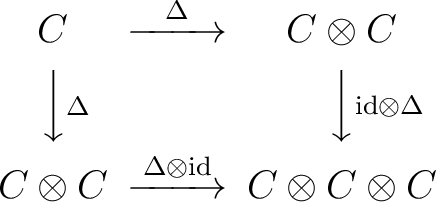 |
(0.2) |
inducing a tangled duality between an associative (unital algebra
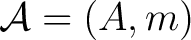 , and an associative (unital) `co–gebra' , and an associative (unital) `co–gebra'
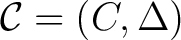 . The idea is to take this structure and combine the Grassmann algebra . The idea is to take this structure and combine the Grassmann algebra
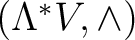 with the `co-gebra' with the `co-gebra'
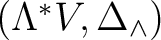 (the `tangled dual') along with the Hopf algebra compatibility rules: 1) the product and the unit are `co–gebra' morphisms, and 2) the coproduct and counit are algebra morphisms. (the `tangled dual') along with the Hopf algebra compatibility rules: 1) the product and the unit are `co–gebra' morphisms, and 2) the coproduct and counit are algebra morphisms.
Next we consider the following ingredients:
| (1) |
the graded switch
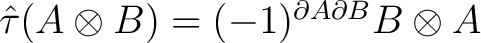 |
| (2) |
the counit
 (an algebra morphism) satisfying (an algebra morphism) satisfying
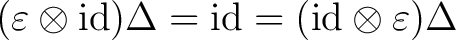 |
| (3) |
the antipode 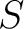 . . |
The Grassmann-Hopf algebra
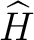 thus consists of–is defined by– the septet thus consists of–is defined by– the septet
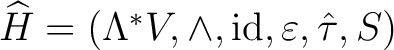 . .
Its generalization to a Grassmann-Hopf algebroidhttp://physicslibrary.org/encyclopedia/Algebroids.html is straightforward by considering a groupoid
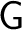 , and then defining a , and then defining a
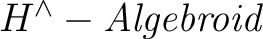 as a quadruple as a quadruple
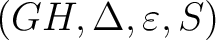 by modifying the Hopf algebroid definition so that by modifying the Hopf algebroid definition so that
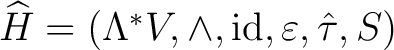 satisfies the standard Grassmann-Hopf algebra axioms stated above. We may also say that satisfies the standard Grassmann-Hopf algebra axioms stated above. We may also say that
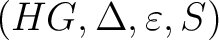 is a weak C*-Grassmann-Hopf algebroid when is a weak C*-Grassmann-Hopf algebroid when
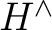 is a unital C*-algebra (with is a unital C*-algebra (with  ). We thus set ). We thus set
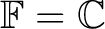 . Note however that the tangled-duals of Grassman-Hopf algebroids retain both the intuitive interactions and the dynamic diagram advantages of their physical, extended symmetry representations exhibited by the Grassman-Hopf al/gebras and co-gebras over those of either weak C*- Hopf algebroids or weak Hopf C*- algebras. . Note however that the tangled-duals of Grassman-Hopf algebroids retain both the intuitive interactions and the dynamic diagram advantages of their physical, extended symmetry representations exhibited by the Grassman-Hopf al/gebras and co-gebras over those of either weak C*- Hopf algebroids or weak Hopf C*- algebras.
- 1
- E. M. Alfsen and F. W. Schultz: Geometry of State Spaces of Operator Algebras, Birkhäuser, Boston–Basel–Berlin (2003).
- 2
- I. Baianu : Categories, Functors and Automata Theory: A Novel Approach to Quantum Automata through Algebraic–Topological Quantum Computations., Proceed. 4th Intl. Congress LMPS, (August-Sept. 1971).
- 3
- I. C. Baianu, J. F. Glazebrook and R. Brown.: A Non–Abelian, Categorical Ontology of Spacetimes and Quantum Gravity., Axiomathes 17,(3-4): 353-408(2007).
- 4
- I.C.Baianu, R. Brown J.F. Glazebrook, and G. Georgescu, Towards Quantum Non–Abelian Algebraic Topology, (2008).
- 5
- F.A. Bais, B. J. Schroers and J. K. Slingerland: Broken quantum symmetry and confinement phases in planar physics, Phys. Rev. Lett. 89 No. 18 (1–4): 181–201 (2002).
- 6
- J.W. Barrett.: Geometrical measurements in three-dimensional quantum gravity. Proceedings of the Tenth Oporto Meeting on Geometry, Topology and Physics (2001). Intl. J. Modern Phys. A 18 , October, suppl., 97–113 (2003)
- 7
- M. Chaician and A. Demichev: Introduction to Quantum Groups, World Scientific (1996).
- 8
- Coleman and De Luccia: Gravitational effects on and of vacuum decay., Phys. Rev. D 21: 3305 (1980).
- 9
- L. Crane and I.B. Frenkel. Four-dimensional topological quantum field theory, Hopf categories, and the canonical bases. Topology and physics. J. Math. Phys. 35 (no. 10): 5136–5154 (1994).
- 10
- W. Drechsler and P. A. Tuckey: On quantum and parallel transport in a Hilbert bundle over spacetime., Classical and Quantum Gravity, 13:611-632 (1996). doi: 10.1088/0264–9381/13/4/004
- 11
- V. G. Drinfel'd: Quantum groups, In Proc. Int. Congress of Mathematicians, Berkeley, 1986, (ed. A. Gleason), Berkeley, 798-820 (1987).
- 12
- G. J. Ellis: Higher dimensional crossed modules of algebras, J. of Pure Appl. Algebra 52: 277-282 (1988), .
- 13
- P.. I. Etingof and A. N. Varchenko, Solutions of the Quantum Dynamical Yang-Baxter Equation and Dynamical Quantum Groups, Comm.Math.Phys., 196: 591-640 (1998).
- 14
- P. I. Etingof and A. N. Varchenko: Exchange dynamical quantum groups, Commun. Math. Phys. 205 (1): 19-52 (1999)
- 15
- P. I. Etingof and O. Schiffmann: Lectures on the dynamical Yang–Baxter equations, in Quantum Groups and Lie Theory (Durham, 1999), pp. 89-129, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2001.
- 16
- B. Fauser: A treatise on quantum Clifford Algebras. Konstanz, Habilitationsschrift.
arXiv.math.QA/0202059 (2002).
- 17
- B. Fauser: Grade Free product Formulae from Grassmann–Hopf Gebras. Ch. 18 in R. Ablamowicz, Ed., Clifford Algebras: Applications to Mathematics, Physics and Engineering, Birkhäuser: Boston, Basel and Berlin, (2004).
- 18
- J. M. G. Fell.: The Dual Spaces of C*–Algebras., Transactions of the American Mathematical Society, 94: 365–403 (1960).
- 19
- F.M. Fernandez and E. A. Castro.: (Lie) Algebraic Methods in Quantum Chemistry and Physics., Boca Raton: CRC Press, Inc (1996).
- 20
- R. P. Feynman: Space–Time Approach to Non–Relativistic Quantum Mechanics, Reviews of Modern Physics, 20: 367–387 (1948). [It is also reprinted in (Schwinger 1958).]
- 21
- A. Fröhlich: Non-Abelian Homological Algebra. I.Derived functors and satellites., Proc. London Math. Soc., 11(3): 239–252 (1961).
- 22
- R. Gilmore: Lie Groups, Lie Algebras and Some of Their Applications., Dover Publs., Inc.: Mineola and New York, 2005.
- 23
- P. Hahn: Haar measure for measure groupoids., Trans. Amer. Math. Soc. 242: 1–33(1978).
- 24
- P. Hahn: The regular representations of measure groupoids., Trans. Amer. Math. Soc. 242:34–72(1978).
- 25
- R. Heynman and S. Lifschitz. 1958. Lie Groups and Lie Algebras., New York and London: Nelson Press.
- 26
- C. Heunen, N. P. Landsman, B. Spitters.: A topos for algebraic quantum theory, (2008)
arXiv:0709.4364v2 [quant–ph]
|
"Grassmann-Hopf algebras and coalgebras\gebras" is owned by bci1.
|
|
| Keywords: |
Grassmann-Hopf algebras, coalgebras\gebras |
Cross-references: representations, dynamic diagram, C*-algebra, Hopf algebroid, groupoid, algebroid, morphisms, Hopf algebra, tangled duality, section, coproduct, duality, relation, generators, identity, vector space
This is version 3 of Grassmann-Hopf algebras and coalgebras\gebras, born on 2009-03-18, modified 2009-03-18.
Object id is 598, canonical name is GrassmannHopfAlgebrasAndCoalgebrasgebras.
Accessed 1112 times total.
Classification:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pending Errata and Addenda
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

