|
Hamiltonian algebroid
|
(Definition)
|
|
Hamiltonian algebroids are generalizations of the Lie algebras of canonical transformations.
Definition 0.1 Let 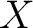 and 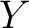 be two vector fields on a smooth manifold 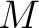 , represented here as operators acting on functions. Their commutator, or Lie bracket, 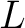 , is :
Moreover, consider the classical configuration space
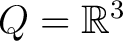 of a classical, mechanical system, or particle whose phase space is the cotangent bundle of a classical, mechanical system, or particle whose phase space is the cotangent bundle
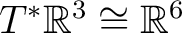 , for which the space of (classical) observables is taken to be the real vector space of smooth functions on , for which the space of (classical) observables is taken to be the real vector space of smooth functions on  , and with T being an element of a Jordan-Lie (Poisson) algebra whose definition is also recalled next. Thus, one defines as in classical dynamics the Poisson algebra as a Jordan algebra in which , and with T being an element of a Jordan-Lie (Poisson) algebra whose definition is also recalled next. Thus, one defines as in classical dynamics the Poisson algebra as a Jordan algebra in which  is associative. We recall that one needs to consider first a specific algebra (defined as a vector space is associative. We recall that one needs to consider first a specific algebra (defined as a vector space 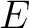 over a ground field (typically over a ground field (typically
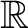 or or
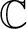 )) equipped with a bilinear and distributive multiplication )) equipped with a bilinear and distributive multiplication  . Then one defines a Jordan algebra (over . Then one defines a Jordan algebra (over
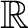 ), as a a specific algebra over ), as a a specific algebra over
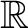 for which: for which:
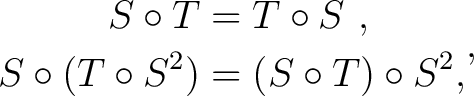
for all elements 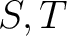 of this algebra. of this algebra.
Then, the usual algebraic types of morphisms automorphism, isomorphism, etc.) apply to a Jordan-Lie (Poisson) algebra defined as a real vector space
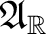 together with a Jordan product together with a Jordan product  and Poisson bracket and Poisson bracket
 , satisfying : , satisfying :
| 1. |
for all
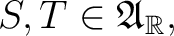
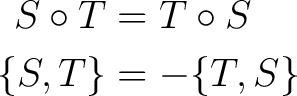
|
| 2. |
the Leibniz rule holds
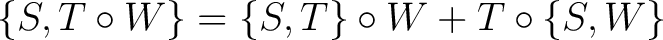 for all for all
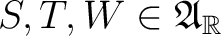 , along with , along with
|
| 3. |
the Jacobi identity :
|
| 4. |
for some
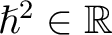 , there is the associator identity : , there is the associator identity :
|
Thus, the canonical transformations of the Poisson sigma model phase space specified by the Jordan-Lie (Poisson) algebra (also Poisson algebra), which is determined by both the Poisson bracket and the Jordan product 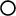 , define a Hamiltonian algebroid with the Lie brackets , define a Hamiltonian algebroid with the Lie brackets 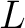 related to such a Poisson structure on the target space. related to such a Poisson structure on the target space.
|
"Hamiltonian algebroid" is owned by bci1.
|
|
See Also: quantum Hamiltonian operator
| Keywords: |
Hamiltonian algebroids |
Cross-references: identity, isomorphism, morphisms, types, algebraic, field, Poisson algebra, dynamics, vector space, observables, system, commutator, functions, operators, manifold, vector fields, Lie algebras
There are 24 references to this object.
This is version 9 of Hamiltonian algebroid, born on 2008-12-16, modified 2009-02-01.
Object id is 333, canonical name is HamiltonianAlgebroid2.
Accessed 2090 times total.
Classification:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pending Errata and Addenda
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

