|
|
|
Main Menu
|
|
Sections
Meta
Talkback
Downloads
Information
|
|
|
|
|
|
D'Alembertian
|
(Definition)
|
|
|
The D'Alembertian is the equivalent of the Laplacian in Minkowskian geometry. It is given by:
Here we assume a Minkowskian metric of the form
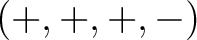 as typically seen in special relativity. The connection between the Laplacian in Euclidean space and the D'Alembertian is clearer if we write both operators and their corresponding metric. as typically seen in special relativity. The connection between the Laplacian in Euclidean space and the D'Alembertian is clearer if we write both operators and their corresponding metric.
Metric: 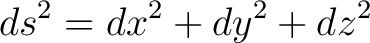 Operator: 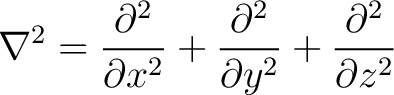 Metric: 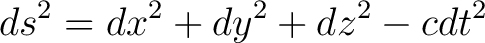 Operator: 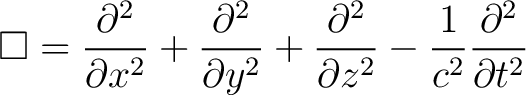 In both cases we simply differentiate twice with respect to each coordinate in the metric. The D'Alembertian is hence a special case of the generalised Laplacian.
The wave equation is given by:
Factorising in terms of operators, we obtain:
or
Hence the frequent appearance of the D'Alembertian in special relativity and electromagnetic theory.
The symbols 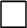 and and  are both used for the D'Alembertian. Since it is unheard of to square the D'Alembertian, this is not as confusing as it may appear. The symbol for the Laplacian, are both used for the D'Alembertian. Since it is unheard of to square the D'Alembertian, this is not as confusing as it may appear. The symbol for the Laplacian, 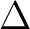 or or 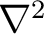 , is often used when it is clear that a Minkowski space is being referred to.
It is common to define Minkowski space to have the metric , is often used when it is clear that a Minkowski space is being referred to.
It is common to define Minkowski space to have the metric
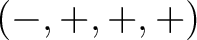 , in which case the D'Alembertian is simply the negative of that defined above: , in which case the D'Alembertian is simply the negative of that defined above:
|
"D'Alembertian" is owned by invisiblerhino.
|
|
See Also: Laplacian in Cartesian Coordinates
| Other names: |
wave operator, D'Alembert operator |
Cross-references: square, wave equation, operators, special relativity, metric, Laplacian
There are 4 references to this object.
This is version 2 of D'Alembertian, born on 2008-03-20, modified 2008-03-20.
Object id is 271, canonical name is DAlembertian.
Accessed 2633 times total.
Classification:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pending Errata and Addenda
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

