|
Lemma.
for all constant values of 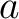 . .
Proof. Let
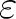 be any positive number. Then we get: be any positive number. Then we get:
as soon as
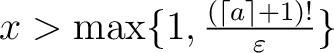 . Here, . Here,
 means the ceiling function; means the ceiling function; 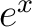 has been estimated downwards by taking only one of the all positive terms of the series expansion has been estimated downwards by taking only one of the all positive terms of the series expansion
theorem. The growth of the real exponential function
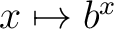 exceeds all power functions, i.e. exceeds all power functions, i.e.
with 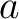 and and 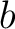 any constants, any constants, 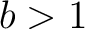 . .
Proof. Since 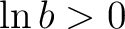 , we obtain by using the lemma the result , we obtain by using the lemma the result
Corollary 1.
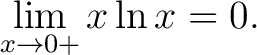
Proof. According to the lemma we get
Corollary 2.
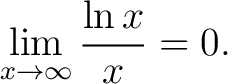
Proof. Change in the lemma 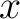 to to 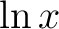 . .
Corollary 3.
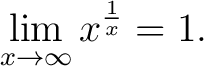 (Cf. limit of nth root of n.) (Cf. limit of nth root of n.)
Proof. By corollary 2, we can write:
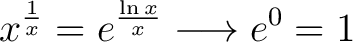 as as
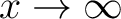 (see also theorem 2 in limit rules of functions). (see also theorem 2 in limit rules of functions).
| 
