|
variable groupoid
|
(Definition)
|
|
|
Remarks An indexed family or class of topological groupoids
![$[\mathsf{G}_i]$ $[\mathsf{G}_i]$](http://images.physicslibrary.org/cache/objects/679/l2h/img8.png) with with 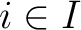 in the category Grpd of groupoids with additional axioms, rules, or properties of the underlying topological groupoids, that specify an indexed family of topological groupoid homomorphisms for each variable groupoid structure. in the category Grpd of groupoids with additional axioms, rules, or properties of the underlying topological groupoids, that specify an indexed family of topological groupoid homomorphisms for each variable groupoid structure.
Besides systems modelled in terms of a fibration of groupoids, one may consider a multiple groupoid defined as a set of 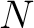 groupoid structures, any distinct pair of which satisfy an interchange law which can be formulated as follows. There exists a unique expression with the following content: groupoid structures, any distinct pair of which satisfy an interchange law which can be formulated as follows. There exists a unique expression with the following content:
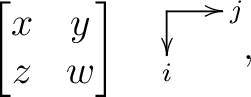 |
(0.1) |
where 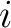 and and 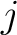 must be distinct for this concept to be well defined. This uniqueness can also be represented by the equation must be distinct for this concept to be well defined. This uniqueness can also be represented by the equation
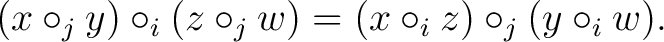 |
(0.2) |
Remarks This illustrates the principle that a 2-dimensional formula may be more comprehensible than a linear one.
Brown and Higgins, 1981a, showed that certain multiple groupoids equipped with an extra structure called connections were equivalent to another structure called a crossed complex which had already occurred in homotopy theory. such as double, or multiple groupoids (Brown, 2004; 2005). For example, the notion of an atlas of structures should, in principle, apply to a lot of interesting, topological and/or algebraic, structures: groupoids, multiple groupoids, Heyting algebras, 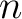 -valued logic algebras and -valued logic algebras and 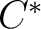 -convolution -algebras. Such examples occur frequently in higher dimensional algebra (HDA). -convolution -algebras. Such examples occur frequently in higher dimensional algebra (HDA).
|
"variable groupoid" is owned by bci1.
|
|
See Also: variable network topology
| Other names: |
variable topological space with groupoid structure |
| Also defines: |
parameter-dependent family of groupoids |
| Keywords: |
variable groupoids, variable topology |
Cross-references: HDA, higher dimensional algebra, algebraic, topological, homotopy theory, crossed complex, formula, concept, systems, homomorphisms, category, topological groupoids, dynamic, parameter, groupoids
This is version 4 of variable groupoid, born on 2009-04-19, modified 2009-04-19.
Object id is 679, canonical name is VariableGroupoid.
Accessed 1806 times total.
Classification:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pending Errata and Addenda
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

