|
topic on computational physics
|
(Topic)
|
|
|
This is a contributed topic on computational physics.
Definition 0.1 Computational Physics is broadly defined as the application of computer programming, as well as of other computational means, such as: algebraic, topological, categorical, logical (including quantum logics, many-valued logics, automata theory), and so on, to obtain physically relevant results –that are often numerical.
One notes that computational physics can also be considered as a major area of applied (computational) mathematics and/or applied physics.
This term is often employed in the more restricted, practical sense of applying computers to obtain numerical solutions to physics problems, or as an illustration to physical processes, phenomena or theories. At the top end of computing resources, supercomputers are beginning to be very widely employed in physics for a variety of reasons, including relatively inexpensive simulations of very important physics problems that cannot be solved at present by any other means. Other, several contributed examples will be considered next in this topic, and are also more precisely defined in the following bibliography (available in part for download from the book and expositions/paper sections of
PlanetPhysics.org).
- Computational fluid dynamics-in rheology;
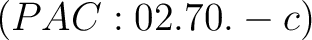
- Computational methods in classical mechanics (
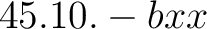 ; see also ; see also 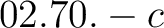 ) )
- Computational techniques in mathematical methods in physics
- Programming languages (Fortran, Basic/TurboBasic/AppleBasic, Algol, Pascal,
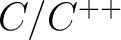 ), programs (Mathematica, Maple, Systat) and OS systems ( ), programs (Mathematica, Maple, Systat) and OS systems (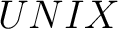 , , 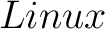 , Windows, , Windows, 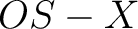 ) employed in Computational Physics ) employed in Computational Physics
- concepts: UTM, quantum automata concepts
- Quantum Computations in: QCD, QFT, AQFT, QED, LQED, LQFT, Quantum Gravity (QG, LQG) computations on a lattice, quantum molecular dynamics (QMD) and quantum chemistry (QC)
- F
- G
- H
- K
- 1
- A Computational Physics –an introductory book
- 2
- A website for Free downloading of Computational Physics books
- 3
- A Computational Physics –An introductory course
|
Anyone with an account can edit this entry. Please help improve it!
"topic on computational physics" is owned by bci1.
|
|
See Also: applied physics, supercomputers, topic on computer programming, superconductivity
| Also defines: |
Computational Physics, computation, UTM, computer program, topological computation, lattice-based computation, Monte-Carlo computation, programming language, QC, QCD, QMD, QED, LQED, LQFT, LQG, C++, UNIX, Linux, Pascal, Java, Fortran, Algol, quantum automaton, quantum logics, automata theory, quantum molecular dynamics, fluid dynamics, superfluid, MC, quantum gravity, QG, LQG |
| Keywords: |
computational physics, computation, UTM, computer program, topological computation, lattice-based computation, Monte-Carlo computation, programming language, computational physics, QC, QCD, QMD, QFT, AQFT, QED, LQED, LQFT, LQG, C++, UNIX, Linux, Pascal, Java, Fortran, Algol, quantum automaton, quantum logics, automata theory, quantum molecular dynamics, fluid dynamics, superfluid, QMD, MC, quantum gravity, QG, LQG, supercomputers |
Cross-references: AQFT, QFT, quantum automata, concepts, systems, OS, programs, classical mechanics, sections, supercomputers, computers, applied physics, many-valued logics, topological, algebraic, computational physics
There are 80 references to this object.
This is version 19 of topic on computational physics, born on 2009-03-04, modified 2009-06-08.
Object id is 573, canonical name is TopicOnComputationalPhysics.
Accessed 16348 times total.
Classification:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pending Errata and Addenda
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

