|
Fundamental physical concepts
|
(Topic)
|
|
- Space,
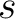
- Time,
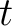
- spacetime,
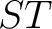
- reference system or Frame of Reference (
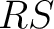 ) )
- Motion
- Measurement
- observable
- Universal constants: Planck's constant (
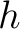 , the speed of light, , the speed of light, 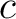 , gravitational constant, , gravitational constant, 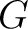 ; hyperfine constant, ; hyperfine constant, 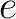 ; cosmological constant, ; cosmological constant, 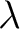 ; Boltzmann constant, ; Boltzmann constant, 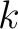 . .
- Matter
- Mass
- Particle
- Elementary Particles and quarks
- Energy: Conservation Laws, Hamiltonian operator, energy eigenvalues. eigenstates, Lagrangian, Photons/Electromagnetic radiation
- Fields: Electromagnetic, magnetic, electrical; nuclear; gravitational; gauge fields; non-Abelian gauge fiel theory
- Gravity
- String/strings
- Oscillatory motion, Oscillation, Periodic and Quasi-periodic motions
- Wave
- Wave function, Hermitian operator, non-Hermitian operator, Super-operator, Prigogine Time operator
- Period of oscillation
- Frequency
- Oscillation
- Force
- Reaction force
- Interactions: strong interactions: quark-quark, quark-pair, quark-gluon, gluon-gluon interactions, etc; Electromagnetic Iiteractions; self-interaction; Electro-weak interactions;gravitational interactions and gravitons
- Potential
- virtual particles
- Kinetics and dynamics, Chaotic Dynamics, Quantum Dynamics
- system: closed, open, dynamic; classical or Newtonian, mechanical, relativistic, Thermodynamic, quantum; simple, chaotic, complex, super-complex, ultra-complex, hyper-complex
- dynamical system
- entropy,
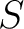
- Mechanical work
- temperature
- heat,

- Enthalpy,
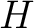
- Partition Function,
- 1
- Isaac Newton. 1686.Principles of Natural Philosophy. “The Principia."
- 2
- G. Gray, ed. 1888. The complete list of “Works of Sir Isaac Newton–Isaaci Newtoni Opera quae exstant omnia".. London, UK. (See also:
 ). ).
- 3
- Albert Einstein. 1956. Relativity Theory. NL
- 4
- Dirac, Paul A.M. 1958. Principles of Quantum Mechanics. NL
- 5
- Richard Feynman. 1965. Lecture Notes in Physics. NL
- 6
- Richard Feynman and Steven Weinberg. 1987. “Elementary Particles and the Laws of Physics: The 1986 Dirac Memorial Lectures”.
- 7
- Steven Weinberg. 1994. “The Quantum Theory of Fields” (three volumes: 1995, 1996, 2003). Nobel Laureate in Theoretical Physics in 1979. “Gravitation and Cosmology: Principles and Applications of the General Theory of Relativity” (1972) “The First Three Minutes: A Modern View of the Origin of the Universe” (1977, updated in 1993, ISBN 0-465-02437-8) “The Discovery of Subatomic Particles” (1983). “Dreams of a Final Theory: The Search for the Fundamental Laws of Nature” (1993), ISBN 0-09-922391-0 “The Quantum Theory of Fields” (three volumes: 1995, 1996, 2003) “Facing Up: Science and Its Cultural Adversaries” (2001, 2003, Harvard University Press, HUP) “Glory and Terror: The Coming Nuclear Danger” (2004, NYRB) “Cosmology” (2008, [[Oxford University Press|OUP]]) “Lake Views: This World and the Universe” (2010), Belknap Press of Harvard University Press, ISBN 0674035151.
- 8
- Weinberg, S., 1967.
 A Model of Leptons, Phys. Rev. Lett. 19, 1264–1266 (1967), his fundamental electroweak unification paper. A Model of Leptons, Phys. Rev. Lett. 19, 1264–1266 (1967), his fundamental electroweak unification paper.
- 9
- Weinberg, S. and G. Feinberg.“Law of Conservation of Muons", Columbia University, University of California–Berkeley, United States Department of Energy (through predecessor agency of the US Atomic Energy Commission, Atomic Energy Commission), (Feb. 1961). Pais, A., Weinberg, S., Quigg, C., Riordan, M., Panofsky, W.K.H. and V. Trimble. “100 years of elementary particles”, Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, (SLAC) United States Department of Energy, “Beam Line”, vol. 27, issue 1, Spring 1997. (April 1, 1997).
 “A Designer Universe?”, critically discussing the possibility of the intelligent design of the universe, is based on a talk given in April 1999 at the Conference on Cosmic Design of the American Association for the Advancement of Science in Washington, D.C. Steven Weinberg. “A Designer Universe?”, critically discussing the possibility of the intelligent design of the universe, is based on a talk given in April 1999 at the Conference on Cosmic Design of the American Association for the Advancement of Science in Washington, D.C. Steven Weinberg.
 Nobel prize autobiography. Nobel prize autobiography.
- 10
- Eilenberg, S., and Kelly, G.M., *Closed Categories, Proceedings of the Conference on Categorical Algebra (La Jolla 1965), Springer Verlag 1966.
- 11
- Eilenberg, S., and Mac Lane, S., *General Theory of Natural Equivalences, Trans. Amer. Math. Soc. 58, 231–294 (1945).
- 12
- Kan, D. M., *Adjoint Functors, Trans. Amer. Math. Soc. 87, 294–329 (1958).
- 13
- Lawvere, F. W., *Functorial Semantics of Algebraic Theories, Proc. Nat. Acad. Sc. U.S.A.,50, 869–872 (1963).
- 13
- Lawvere, F. W., *The Category of Categories as a Foundation for Mathematics, Proceedings of the Conference on Categorical Algebra (La Jolla 1965), Springer Verlag. 1966.
(See also the Review 7332 by J. Isbell, Dec. 1967, Math. Reviews).
- 14
- Mac Lane, S., *Categorical Algebra, Bull. Amer. Math. Soc., 71, 40–106 (1965).
- 10
- Eilenberg, S., and Kelly, G.M., *Closed Categories, Proceedings of the Conference on Categorical Algebra (La Jolla 1965), Springer Verlag 1966.
*1. Unlike Mathematical Axioms that have all terms defined mathematically, the Axioms of Physics, oftentimes called “Postulates”, are defined in terms of physical concepts that may also relate to measurements and may include basic physical assumptions derived on an experimental and physical-conceptual basis, such as the fundamental axiom of Local Quantum Field Theory, or Axiomatic Quantum Field Theory, also called Algebraic Quantum Field Theory (AQFT), that all quantum measurements and observations involve local interactions in spacetime.
|
Anyone with an account can edit this entry. Please help improve it!
"Fundamental physical concepts" is owned by bci1.
|
|
See Also: Space and Time in Classical Mechanics, The System of Co-ordinate, wave equation, dynamical system, The Gravitational Field, Relativity: The Special and General Theory, Thermodynamics, Axioms of Physics
| Also defines: |
fundamental physical concepts, subatomic particles, Physics axioms, local interactions, quantum measurement, Local Quantum Physics, Algebraic Quantum Field Theory, AQFT, Axiomatic Quantum Field Theory, HQFT, fundamental physics concepts, energy, field, wave, mass, universal constant, speed of light, reference frame, Lorentz transformations, Poincare' transformations group, Lorentz group of transformations, energy-mass law, quantum fields, gauhe fields, non-Abelian physical theories, motion, universal constant, cosmological constant, SLAC |
| Keywords: |
local interactions, quantum measurement, Local Quantum Physics, Algebraic Quantum Field Theory, AQFT, Axiomatic Quantum Field Theory, HQFT, fundamental physics concepts, energy, field, wave, mass, universal constant, speed of light, reference frame, Lorentz transformations, Poincare' transformations group, Lorentz group of transformations, energy-mass law, quantum fields, gauhe fields, non-Abelian physical theories, motion, universal constant, cosmological constant |
Cross-references: heat, temperature, work, entropy, dynamical system, Thermodynamic, system, dynamics, gravitons, strong interactions, operator, function, non-Abelian, radiation, Lagrangian, Hamiltonian operator, quarks, Boltzmann constant, observable, reference system, spacetime
There are 206 references to this object.
This is version 17 of Fundamental physical concepts, born on 2010-10-31, modified 2010-10-31.
Object id is 887, canonical name is FundamentalPhysicalConcepts.
Accessed 2708 times total.
Classification:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pending Errata and Addenda
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

