|
|
|
The concept of category emerged in 1943-1945 from work in algebraic topology and Homological Algebra by S. Eilenberg and S. Mac Lane [29], as a generalization of the algebraic concepts of semigroup, monoid, group, groupoid, etc., as well as an extension
of topological concepts and diagrams employed in algebraic topology and homological algebra. Thus many properties of mathematical systems can be unified by a presentation with diagrams of arrows that may represent functions, transformations, distributions, operators, etc., and that– in the case of concrete categories– may also include objects such as class elements, sets, topological spaces, etc. ; the usefulness of such diagrams comes from the composition of the arrows and the (fundamental) axioms that define any category which allow mathematical constructions to be represented by universal properties of diagrams.
To introduce the modern concept of category, according to S. MacLane [27] without using any set theory, one needs to introduce first the notions of metagraph and metacategory.
Definition 0.3 A category
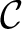 is an interpretation of a metacategory within set theory. Thus, a category is a graph – defined by a set
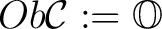 , a set of arrows* (called also morphisms)
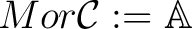 , and two functions:
and
– that also has two additional functions:
defined by the assignments
called identity, and a composition
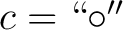 , that is,
, defined by the assignments
 , such that:
for all objects
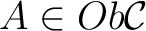 and all composable pairs of arrows (morphisms)
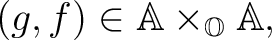 and also such that the unit law and associativity axioms c1 and c2 hold.
*Note that the set of all morphisms
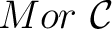 of a category of a category
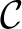 is sometimes denoted as is sometimes denoted as
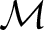 , or in French publications as , or in French publications as
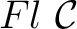 . .
For convenience one also defines a 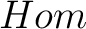 (or (or 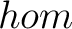 ) set as: ) set as:
which is also denoted as
![$[B,C]_\mathcal{C}$ $[B,C]_\mathcal{C}$](http://images.physicslibrary.org/cache/objects/634/l2h/img50.png) , or simply , or simply ![$[B,C].$ $[B,C].$](http://images.physicslibrary.org/cache/objects/634/l2h/img51.png) There are several alternative definitions of a category. Thus, as defined by W.F. Lawvere, a category is an interpretation of the ETAC axioms from his elementary theory of abstract categories [26]. For small categories– whose
There are several alternative definitions of a category. Thus, as defined by W.F. Lawvere, a category is an interpretation of the ETAC axioms from his elementary theory of abstract categories [26]. For small categories– whose
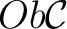 is a set and also is a set and also
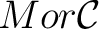 is a set– one has a direct definition. is a set– one has a direct definition.
If, on the other hand,
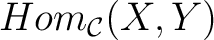 is a class rather than a set then the category is a class rather than a set then the category
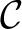 is called large. is called large.
- 1
- Baez, J. & Dolan, J., 1998a, Higher-Dimensional Algebra III. n-Categories and the Algebra of Opetopes, in: Advances in Mathematics, 135, 145–206.
- 2
- Baez, J. & Dolan, J., 1998b, “Categorification", Higher Category Theory, Contemporary Mathematics, 230, Providence: AMS, 1–36.
- 3
- Baez, J. & Dolan, J., 2001, From Finite Sets to Feynman Diagrams, in Mathematics Unlimited – 2001 and Beyond, Berlin: Springer, 29–50.
- 4
- Baez, J., 1997, An Introduction to n-Categories, in Category Theory and Computer Science, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 1290, Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 1–33.
- 5
- Baianu, I. and M. Marinescu: 1968, Organismic Supercategories: Towards a Unitary Theory of Systems. Bulletin of Mathematical Biophysics 30, 148-159.
- 6
- Baianu, I.C.: 1970, Organismic Supercategories: II. On Multistable Systems. Bulletin of Mathematical Biophysics, 32: 539-561.
- 7
- Baianu,I.C. : 1971a, Organismic Supercategories and Qualitative Dynamics of Systems. Ibid., 33 (3), 339–354.
- 8
- I.C. Baianu: 1971b, Categories, Functors and Quantum Algebraic Computations, in P. Suppes (ed.), Proceed. Fourth Intl. Congress Logic-Mathematics-Philosophy of Science, September 1–4, 1971, University of Bucharest.
- 9
- I.C. Baianu: Łukasiewicz-Topos Models of Neural Networks, Cell Genome and Interactome Nonlinear Dynamics). CERN Preprint EXT-2004-059. Health Physics and Radiation Effects (June 29, 2004).
- 10
- I.C. Baianu and D. Scripcariu: 1973, On Adjoint Dynamical Systems. The Bulletin of Mathematical Biophysics, 35(4), 475–486.
- 11
- I.C. Baianu: 1973, Some Algebraic Properties of (M,R) – Systems. Bulletin of Mathematical Biophysics 35, 213-217.
- 12
- I.C. Baianu and M. Marinescu: 1974, A Functorial Construction of (M,R)– Systems. Revue Roumaine de Mathematiques Pures et Appliquees 19: 388-391.
- 13
- I.C. Baianu: 1977, A Logical Model of Genetic Activities in Łukasiewicz Algebras: The Non-linear Theory. Bulletin of Mathematical Biophysics, 39: 249-258.
- 14
- I.C. Baianu: 1980, Natural Transformations of Organismic Structures. Bulletin of Mathematical Biophysics 42: 431-446.
- 15
- Baianu, I.C.: 1987. Mathematical Models in Medicine, vol. 7., Ch.11 Pergamon Press, New York, 1513 -1577; URLs: CERN Preprint No. EXT-2004-072:, available here as PDF, or as as an archived html document.
- 16
- Baianu, I. C., Glazebrook, J. F. and G. Georgescu: 2004, Categories of Quantum Automata and N-Valued Łukasiewicz Algebras in Relation to Dynamic Bionetworks, (M,R)–Systems and Their Higher Dimensional Algebra, PDF's of Abstract and Preprint of Report.
- 17
- Baianu, I.C. Brown R., J. F. Glazebrook, and Georgescu G.: 2006, Complex Nonlinear Biodynamics in Categories, Higher Dimensional Algebra and Łukasiewicz–Moisil Topos: Transformations of Neuronal, Genetic and Neoplastic networks, Axiomathes 16 Nos. 1–2, 65–122.
- 18
- Baianu, I.C., R. Brown and J. F. Glazebrook: 2007b, A Non-Abelian, Categorical Ontology of Spacetimes and Quantum Gravity, Axiomathes, 17: 169-225.
- 28
- Eilenberg, S. and S. Mac Lane.: 1942, Natural Isomorphisms in Group Theory., American Mathematical Society 43: 757-831.
- 20
- Eilenberg, S. and S. Mac Lane: 1945, The General Theory of Natural Equivalences, Transactions of the American Mathematical Society 58: 231-294.
- 21
- Eilenberg, S. & Cartan, H., 1956, Homological Algebra, Princeton: Princeton University Press.
- 22
- Grothendieck, A. et al., Séminaire de Géométrie Algébrique, Vol. 1–7, Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
- 23
- Grothendieck, A., 1957, "Sur Quelques Points d'algèbre homologique", Tohoku Mathematics Journal, 9, 119–221.
- 24
- Lawvere, F. W., 1964, "An Elementary Theory of the Category of Sets", Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences U.S.A., 52, 1506–1511.
- 25
- Lawvere, F. W., 1965, "Algebraic Theories, Algebraic Categories, and Algebraic Functors", Theory of Models, Amsterdam: North Holland, 413–418.
- 26
- Lawvere, F. W., 1966, "The Category of Categories as a Foundation for Mathematics", Proceedings of the Conference on Categorical Algebra, La Jolla, New York: Springer-Verlag, 1–21.
- 27
- MacLane, S., 1997, Categories for the Working Mathematician, 2nd edition, New York: Springer-Verlag.
- 28
- Eilenberg, S. and S. Mac Lane.: 1942, Natural Isomorphisms in Group Theory., American Mathematical Society 43: 757-831.
- 29
- Eilenberg, S. and S. Mac Lane: 1945, The General Theory of Natural Equivalences, Transactions of the American Mathematical Society 58: 231-294.
- 30
- Baianu I. C., Brown R., Georgescu G. and J. F. Glazebrook: 2006b, Complex Nonlinear Biodynamics in Categories, Higher Dimensional Algebra and Łukasiewicz–Moisil Topos: Transformations of Neuronal, Genetic and Neoplastic Networks., Axiomathes, 16 Nos. 1–2: 65–122.
- 31
- Rosen, R.: 1958a, A Relational Theory of Biological Systems., Bulletin of Mathematical Biophysics 20: 245-260.
- 32
- Rosen, R.: 1958b, The Representation of Biological Systems from the Standpoint of the Theory of Categories., Bulletin of Mathematical Biophysics 20: 317-341.
- 33
- See also a more extensive category theory bibliography
|
"category" is owned by bci1.
|
|
See Also: groupoid, categorical sequence, square diagram, commutative square diagram, graph, supercategory, category, categorical diagrams defined as functors, categorical physics, index of algebraic topology, category theory, axiomatic theories of metacategories and supercategories, algebraic topology
| Also defines: |
metagraph, metacategory, category axioms, large category, small category, 4Hom (X, Y)$, unit law, associativity axioms, identity, composition, operations, categorification, groupoidification, graph, dom, cod |
| Keywords: |
category theory, metagraph, metacategory, algebraic topology, homology theory, category, unit law, associativity axioms, identity, composition, operations, graph, dom, cod |
Cross-references: elementary theory of abstract categories, ETAC axioms, morphisms, codomain, domain, objects, operators, functions, systems, diagrams, topological, groupoid, group, monoid, semigroup, algebraic, algebraic topology, work, concept
There are 221 references to this object.
This is version 44 of category, born on 2009-04-06, modified 2009-05-02.
Object id is 634, canonical name is Category.
Accessed 8082 times total.
Classification:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pending Errata and Addenda
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

