|
|
|
Main Menu
|
|
Sections
Meta
Talkback
Downloads
Information
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dirac notations-delta and observable algebras
|
(Topic)
|
|
|
[This is a contributed topic entry in progress on Dirac notations and quantum observable algebras.]
- Introduction
(In progress.)
- non-Abelian (or non-commutative) observable (Clifford) Algebra
(In progress.)
- Dirac notations:
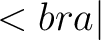 c c 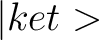 and delta and delta
The Dirac notation (or “bra-ket” notation as commonly known in physics) is used to represent quantum states in quantum mechanics. It was invented by Physics Nobel Laureate Paul A. M. Dirac, and since then has been established as one of the preferred notations in quantum mechanics.
The Dirac notation denotes both the “ket” vector– defined as 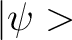 – and its transpose vector– defined as – and its transpose vector– defined as 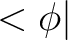 (or “bra” vector). Thus, a “bra-ket” is defined as the inner product of the two vectors defined above, which is denoted as (or “bra” vector). Thus, a “bra-ket” is defined as the inner product of the two vectors defined above, which is denoted as
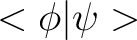 . .
Then, the Dirac notation also satisifies the following identities:
where
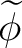 is the “complex conjugate” of is the “complex conjugate” of 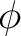 . .
- 1
- Paul A.M. Dirac. 1968. Principles of Quantum Mechanics, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK
|
"Dirac notations-delta and observable algebras" is owned by bci1. [ full author list (2) | owner history (1) ]
|
|
See Also: Dirac equation
| Other names: |
bra-ket notation |
| Also defines: |
Dirac notation |
| Keywords: |
Dirac relativistic field equations, notation, and non-commutative observable algebra |
Cross-references: identities, inner product, vector, quantum mechanics, observable, non-commutative, non-Abelian, quantum observable
This is version 24 of Dirac notations-delta and observable algebras, born on 2006-05-30, modified 2009-01-31.
Object id is 180, canonical name is DiracNotation.
Accessed 3863 times total.
Classification:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pending Errata and Addenda
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

