|
quantized Riemann spaces
|
(Topic)
|
|
|
An interesting, but perhaps limiting approach to quantum gravity (QG), involves defining a quantum Riemannian geometry [2] in place of the classical Riemannian manifold that is employed in the well-known, Einstein's classical approach to general relativity (GR). Whereas a classical Riemannian manifold has a metric defined by a special, Riemannian tensor, the quantum Riemannian geometry may be defined in different theoretical approaches to QG by either quantum loops (or perhaps `strings'), or spin networks and spin foams (in locally covariant GR quantized space-times). The latter two concepts are related to the `standard' quantum spin observables and thus have the advantage of precise mathematical definitions. As
spin foams can be defined as functors of spin network categories, quantized space-times (QST)s can be represented by, or defined in terms of, natural transformations of `spin foam' functors. The latter definition is not however the usual one adopted for quantum Riemannian geometry, and other (for example, noncommutative geometry) approaches attempt to define a QST metric not by a Riemannian tensor –as in the classical GR case– but in relation to a generalized, quantum `Dirac' operator in a spectral triplet.
Remarks. Other approaches to Quantum Gravity include: loop quantum gravity (LQG), AQFT approaches, topological quantum field theory (TQFT)/ homotopy Quantum Field Theories (HQFT; Tureaev and Porter, 2005),
quantum theories on a lattice (QTL), string theories and spin network models.
A Result for quantum spin foam representations of quantum space-times (QST)s: There exists an 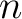 -connected CW model -connected CW model 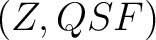 for the pair for the pair 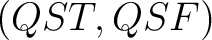 such that: such that:
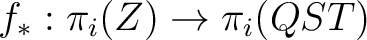 , is an isomorphism for , is an isomorphism for 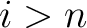 , and it is a monomorphism for , and it is a monomorphism for 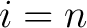 . The . The 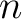 -connected CW model is unique up to homotopy equivalence. (The -connected CW model is unique up to homotopy equivalence. (The 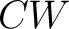 complex, complex, 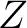 ,
considered here is a homotopic `hybrid' between QSF and QST). ,
considered here is a homotopic `hybrid' between QSF and QST).
- 1
- A. Connes. 1994. Noncommutative Geometry. Academic Press: New York and London.
- 2
- Abhay Ashtekar and Jerzy Lewandowski.2005. Quantum Geometry and Its Applications. PDF file download.
|
"quantized Riemann spaces" is owned by bci1.
|
|
| Keywords: |
quantized Riemann spaces, noncommutative geometry |
Cross-references: monomorphism, isomorphism, quantum space-times, representations, quantum spin foam, SUSY, algebraic topology, theoretical physics, field, quantum geometry, string theories, QTL, quantum theories on a lattice, HQFT, homotopy, TQFT, quantum field theory, topological, AQFT, LQG, loop quantum gravity, operator, relation, noncommutative geometry, spin foam, natural transformations, QST, categories, spin network, functors, spin foams, observables, spin, concepts, spin networks and spin foams, tensor, metric, GR, general relativity, Einstein's, manifold, quantum Riemannian geometry, QG, quantum gravity
This is version 2 of quantized Riemann spaces, born on 2008-10-03, modified 2008-10-14.
Object id is 303, canonical name is QuantizedRiemannSpaces.
Accessed 432 times total.
Classification:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pending Errata and Addenda
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

