|
The position of an object is its location. It is usually denoted as 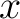 . When working in more than one dimension, position may be considered as a vector quantity; it can then be denoted as . When working in more than one dimension, position may be considered as a vector quantity; it can then be denoted as
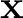 . .
Position is frequently considered as a function of time. In the one-dimensional case, the notations 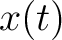 and (more rarely) and (more rarely) 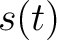 are used. On the other hand, when working in more than one dimension, the notation are used. On the other hand, when working in more than one dimension, the notation
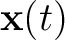 is used. is used.
The SI unit of position is
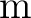 (meters). (meters).
| 
