|
|
|
Main Menu
|
|
Sections
Meta
Talkback
Downloads
Information
|
|
|
|
|
|
determination of Fourier coefficients
|
(Algorithm)
|
|
|
Suppose that the real function 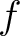 may be presented as sum of the Fourier series: may be presented as sum of the Fourier series:
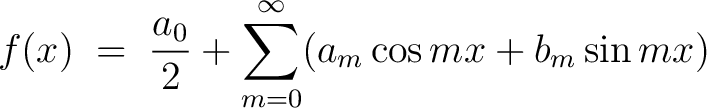 |
(1) |
Therefore, 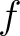 is periodic with period is periodic with period 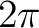 . For expressing the Fourier coefficients . For expressing the Fourier coefficients 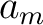 and and 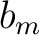 with the function itself, we first multiply the series (1) by with the function itself, we first multiply the series (1) by 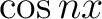 ( (
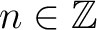 ) and integrate from ) and integrate from 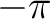 to to 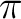 . Supposing that we can integrate termwise, we may write . Supposing that we can integrate termwise, we may write
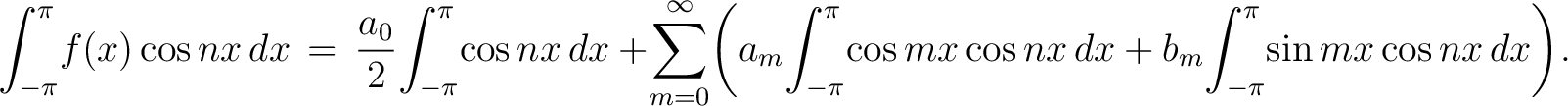 |
(2) |
When 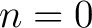 , the equation (2) reads , the equation (2) reads
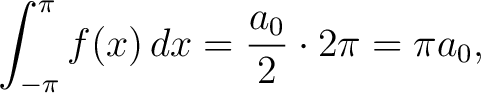 |
(3) |
since in the sum of the right hand side, only the first addend is distinct from zero.
When 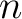 is a positive integer, we use the product formulas of the trigonometric identities, getting is a positive integer, we use the product formulas of the trigonometric identities, getting
The latter expression vanishes always, since the sine is an odd function. If 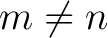 , the former equals zero because the antiderivative consists of sine terms which vanish at multiples of , the former equals zero because the antiderivative consists of sine terms which vanish at multiples of 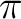 ; only in the case ; only in the case 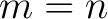 we obtain from it a non-zero result we obtain from it a non-zero result 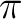 . Then (2) reads . Then (2) reads
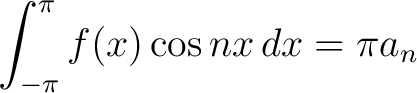 |
(4) |
to which we can include as a special case the equation (3).
By multiplying (1) by 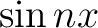 and integrating termwise, one obtains similarly and integrating termwise, one obtains similarly
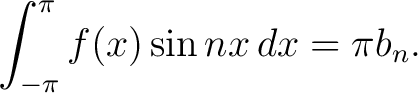 |
(5) |
The equations (4) and (5) imply the formulas
and
for finding the values of the Fourier coefficients of 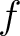 . .
|
Anyone with an account can edit this entry. Please help improve it!
"determination of Fourier coefficients" is owned by pahio. [ full author list (2) ]
|
|
See Also: generalized Fourier transform, generalized Fourier and measured groupoid transforms, 2D-FT MR- Imaging and related Nobel awards
| Keywords: |
Fourier series coefficients, discrete Fourier transform |
Cross-references: identities, formulas, function
This is version 3 of determination of Fourier coefficients, born on 2009-04-18, modified 2009-04-18.
Object id is 660, canonical name is DeterminationOfFourierCoefficients.
Accessed 1112 times total.
Classification:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pending Errata and Addenda
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

