|
The backdrop for the motions of the "wanderers" in the sky is the canopy of stars. If there were no clouds in the sky and we were on a flat plain with nothing to obstruct our view, we could see about 3000 stars with the unaided eye. To find their way around such a multitude, the ancients found groupings of stars that made some familiar geometric pattern or (more rarely) resembled something they knew. Each civilization found its own patterns in the stars, much like a modern Rorschach test in which you are asked to discern patterns or pictures in a set of inkblots. The ancient Chinese, Egyptians, and Greeks, among others, found their own groupings or constellations of stars. These were helpful in navigating among the stars and in passing their star lore on to their children.
You may be familiar with some of the old star patterns we still use today, such as the Big Dipper, Little Dipper, and Orion the hunter, with his distinctive belt of three stars (Figure 1). However, many of the stars we see are not part of a distinctive star pattern at all, and a telescope reveals millions of stars too faint for the eye to see. Therefore, during the early decades of the 20th century, astronomers from many countries decided to establish a more formal system for organizing the sky.
Figure: 1. Orion. (a) The winter constellation of Orion, the hunter, is surrounded by neighboring constellations, as illustrated in the seventeenth-century atlas by Hevelius. (b) A photograph shows the Orion region in the sky. Note the three blue stars that make up the belt of the hunter. The bright red star above the belt denotes his armpit and is called Betelgeuse (pronounced "Beetel-juice"). The bright blue star below the belt is his foot and is called Rigel. (credit a: modification of work by Johannes Hevelius; b: modification of work by Matthew Spinelli)
|
|
Today, we use the term constellation to mean one of 88 sectors into which we divide the sky, much as the United States is divided into 50 states. The modern boundaries between the constellations are imaginary lines in the sky running north-south and east-west, so that each point in the sky falls in a specific constellation, although, like the states, not all constellations are the same size. Whenever possible, we have named each modern constellation after the Latin translations of one of the ancient Greek star patterns that lies within it. Thus, the modern constellation of Orion is a kind of box on the sky, which includes, among many other objects, the stars that made up the ancient picture of the hunter. Some people use the term asterism to denote an especially noticeable star pattern within a
constellation (or sometimes spanning parts of several constellations). For example, the Big Dipper is an asterism within the constellation of Ursa Major, the Big Bear.
Students are sometimes puzzled because the constellations seldom resemble the people or animals for which they were named. In all likelihood, the Greeks themselves did not name groupings of stars because they looked like actual people or subjects (any more than the outline of Washington state resembles George Washington). Rather, they named sections of the sky in honor of the characters in their mythology and then fit the star configurations to the animals and people as best they could.
| Constellation (Latin name) |
Genitive Case Ending |
English Name or Description |
Abbreviation |
Approximate position:
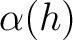 |
Approximate Position:
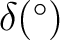 |
|
| Andromeda |
Andromedae |
Princess of Ethiopia |
And |
1 |
+40 |
|
| Antila |
Antilae |
Air pump |
Ant |
10 |
-35 |
|
| Apus |
Apodis |
Bird of Paradise |
Aps |
16 |
-75 |
|
| Aquarius |
Aquarii |
Water bearer |
Aqr |
23 |
-15 |
|
| Aquila |
Aquilae |
Eagle |
Aql |
20 |
+5 |
|
| Ara |
Arae |
Altar |
Ara |
17 |
-55 |
|
| Aries |
Arietis |
Ram |
Ari |
3 |
+20 |
|
| Auriga |
Aurigae |
Charioteer |
Aur |
6 |
+40 |
|
| Bootes |
Bootis |
Herdsman |
Boo |
15 |
+30 |
|
| Caelum |
Cael |
Graving tool |
Cae |
5 |
-40 |
|
| Camelopardus |
Camelopardis |
Giraffe |
Cam |
6 |
+70 |
|
| Cancer |
Cancri |
Crab |
Cnc |
9 |
+20 |
|
| Canes Venatici |
Canum Venaticorum |
Hunting dogs |
CVn |
13 |
+40 |
|
| Canis Major |
Canis Majoris |
Big dog |
CMa |
7 |
-20 |
|
| Canis Minor |
Canis Minoris |
Little dog |
CMi |
8 |
+5 |
|
| Capricornus |
Capricorni |
Sea goat |
Cap |
21 |
-20 |
|
| Carina1 |
Carinae |
Keel of Argonauts' ship |
Car |
9 |
-60 |
|
| Cassiopeia |
Cassiopeiae |
Queen of Ethiopia |
Cas |
1 |
+60 |
|
| Centaurus |
Centauri |
Centaur |
Cen |
13 |
-50 |
|
| Cepheus |
Cephei |
King of Ethiopia |
Cep |
22 |
+70 |
|
| Cetus |
Ceti |
Sea monster (whale) |
Cet |
2 |
-10 |
|
| Chamaeleon |
Chamaeleontis |
Chameleon |
Cha |
11 |
-80 |
|
| Circinus |
Circini |
Compasses |
Cir |
15 |
-60 |
|
| Columba |
Columbae |
Dove |
Col |
6 |
-35 |
|
| Coma Berenices |
Comae Berenices |
Berenice's hair |
Com |
13 |
+20 |
|
| Corona Australis |
Coronae Australis |
Southern crown |
CrA |
19 |
-40 |
|
| Corona Borealis |
Coronae Borealis |
Northern crown |
CrB |
16 |
+30 |
|
| Corvus |
Corvi |
Crow |
Crv |
12 |
-20 |
|
| Crater |
Crateris |
Cup |
Crt |
11 |
-15 |
|
| Crux |
Crucis |
Cross (southern) |
Cru |
12 |
-60 |
|
| Cygnus |
Cygni |
Swan |
Cyg |
21 |
+40 |
|
| Delphinus |
Delphini |
Porpoise |
Del |
21 |
+10 |
|
| Dorado |
Doradus |
Swordfish |
Dor |
5 |
-65 |
|
| Draco |
Draconis |
Dragon |
Dra |
17 |
+65 |
|
| Equuleus |
Equulei |
Little horse |
Equ |
21 |
+10 |
|
| Eridanus |
Eridani |
River |
Eri |
3 |
-20 |
|
| Fornax |
Fornacis |
Furnace |
For |
3 |
-30 |
|
| Gemini |
Geminorum |
Twins |
Gem |
7 |
+20 |
|
| Grus |
Gruis |
Crane |
Gru |
22 |
-45 |
|
| Hercules |
Herculis |
Hercules, son of Zeus |
Her |
17 |
+30 |
|
| Horologium |
Horologii |
Clock |
Hor |
3 |
-60 |
|
| Hydra |
Hydrae |
Sea serpent |
Hya |
10 |
-20 |
|
| Hydrus |
Hydri |
Water snake |
Hyi |
2 |
-75 |
|
| Indus |
Indi |
Indian |
Ind |
21 |
-55 |
|
| Lacerta |
Lacertae |
Lizard |
Lac |
22 |
+45 |
|
| Leo |
Leonis |
Lion |
Leo |
11 |
+15 |
|
| Leo Minor |
Leonis Minoris |
Little lion |
LMi |
10 |
+35 |
|
| Lepus |
Leporis |
Hare |
Lep |
6 |
-20 |
|
| Libra |
Librae |
Balance |
Lib |
15 |
-15 |
|
| Lupus |
Lupi |
Wolf |
Lup |
15 |
-45 |
|
| Lynx |
Lyncis |
Lynx |
Lyn |
8 |
+45 |
|
| Lyra |
Lyrae |
Lyre or harp |
Lyr |
19 |
+40 |
|
| Mensa |
Mensae |
Table Mountain |
Men |
5 |
-80 |
|
| Microscopium |
Microscopii |
Microscope |
Mic |
21 |
-35 |
|
| Monoceros |
Monocerotis |
Unicorn |
Mon |
7 |
-5 |
|
| Musca |
Muscae |
Fly |
Mus |
12 |
-70 |
|
| Norma |
Normae |
Carpenter's level |
Nor |
16 |
-50 |
|
| Octans |
Octantis |
Octant |
Oct |
22 |
-85 |
|
| Ophiuchus |
Ophiuchi |
Holder of serpent |
Oph |
17 |
0 |
|
| Orion |
Orionis |
Orion, the hunter |
Ori |
5 |
+5 |
|
| Pavo |
Pavonis |
Peacock |
Pav |
20 |
-65 |
|
| Pegasus |
Pegasi |
Pegasus, the winged horse |
Peg |
22 |
+20 |
|
| Perseus |
Persei |
Perseus, hero who saved Andromeda |
Per |
3 |
+45 |
|
| Phoenix |
Phoenicis |
Phoenix |
Phe |
1 |
-50 |
|
| Pictor |
Pictoris |
Easel |
Pic |
6 |
-55 |
|
| Pisces |
Piscium |
Fishes |
Psc |
1 |
+15 |
|
| Piscis Austrinus |
Piscis Austrini |
Southern fish |
PsA |
22 |
-30 |
|
| Puppis2 |
Puppis |
Stern of the Argonauts' ship |
Pup |
8 |
-40 |
|
| Pyxis3 (=Malus) |
Pyxidus |
Compass of the Argonauts' ship |
Pyx |
9 |
-30 |
|
| Reticulum |
Reticuli |
Net |
Ret |
4 |
-60 |
|
| Sagitta |
Sagittae |
Arrow |
Sge |
20 |
+10 |
|
| Sagittarius |
Sagittarii |
Archer |
Sgr |
19 |
-25 |
|
| Scorpius |
Scorpii |
Scorpion |
Sco |
17 |
-40 |
|
| Sculptor |
Sculptoris |
Sculptor's tools |
Scl |
0 |
-30 |
|
| Scutum |
Scuti |
Shield |
Sct |
19 |
-10 |
|
| Serpens |
Serpentis |
Serpent |
Ser |
17 |
0 |
|
| Sextans |
Sextantis |
Sextant |
Sex |
10 |
0 |
|
| Taurus |
Tauri |
Bull |
Tau |
4 |
+15 |
|
| Telescopium |
Telescopii |
Telescope |
Tel |
19 |
-50 |
|
| Triangulum |
Trianguli |
Triangle |
Tri |
2 |
+30 |
|
| Triangulum Australe |
Trianguli Australis |
Southern triangle |
TrA |
16 |
-65 |
|
| Tucana |
Tucanae |
Toucan |
Tuc |
0 |
-65 |
|
| Ursa Major |
Ursae Majoris |
Big bear |
UMa |
11 |
+50 |
|
| Ursa Minor |
Ursae Minoris |
Little bear |
UMi |
15 |
+70 |
|
| Vela4 |
Velorum |
Sail of the Argonauts' ship |
Vel |
9 |
-50 |
|
| Virgo |
Virginis |
Virgin |
Vir |
13 |
0 |
|
| Volans |
Volantis |
Flying fish |
Vol |
8 |
-70 |
|
| Vulpecula |
Vulpeculae |
Fox |
Vul |
20 |
+25 |
|
This article is a derivative work of the creative commons share alike with attribution in [1].
- [1] Fraknoi, Andrew, David Morrison, and Sidney Wolff. The Sky Above. In Astronomy 2e. Houston, Texas : OpenStax, 2022. The Sky Above
|

