|
|
|
Main Menu
|
|
Sections
Meta
Talkback
Downloads
Information
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A soliton is a non-linear object which moves through space without dispersion at constant speed. They occur naturally as solutions to the Korteweg - de Vries equation. They were first observed by John Scott Russell in the 19th century and then by Martin Kruskal and Norman Zabusky (who coined the term soliton) in a famous computer simulation in 1965. Insight into solitons can be obtained by noting that the Korteweg - de Vries equation satisfies D'Alembert's solution:
We see at once that this satisfies two important criteria: it has a constant velocity 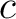 , and it can also be shown that the two functions , and it can also be shown that the two functions 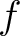 and and 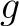 can collide without altering shape. Solitons also occur in non-linear optics and as solutions to field equations in quantum field theory. can collide without altering shape. Solitons also occur in non-linear optics and as solutions to field equations in quantum field theory.
|
"soliton" is owned by invisiblerhino.
|
|
Cross-references: quantum field theory, field, functions, velocity, computer simulation, speed, object
There are 4 references to this object.
This is version 1 of soliton, born on 2008-03-20.
Object id is 273, canonical name is Soliton.
Accessed 1447 times total.
Classification:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pending Errata and Addenda
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

