|
quantum Hamiltonian operator
|
(Definition)
|
|
|
Definition 0.1 The Hamiltonian operator H introduced in quantum mechanics by Schrödinger (and thus sometimes also called the Schrödinger operator) on the Hilbert space
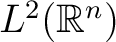 is given by the action: is given by the action:
![$\displaystyle \psi \mapsto [-\nabla^2 +V(x)]\psi, \quad\psi\in L^2(\mathbb{R}^n), $ $\displaystyle \psi \mapsto [-\nabla^2 +V(x)]\psi, \quad\psi\in L^2(\mathbb{R}^n), $](http://images.physicslibrary.org/cache/objects/301/l2h/img2.png) The operator defined above
![$[-\nabla^2 +V(x)]$ $[-\nabla^2 +V(x)]$](http://images.physicslibrary.org/cache/objects/301/l2h/img3.png) , for a potential function , for a potential function 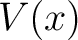 specified as the real-valued function specified as the real-valued function
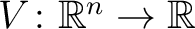 is called the Hamiltonian operator, H, and only very rarely the Schrödinger operator. The energy conservation (quantum) law written with the operator H as the Schrödinger equation is fundamental in quantum mechanics and is perhaps the most utilized, mathematical computation device in quantum mechanics of systems with a finite number of degrees of freedom. There is also, however, the alternative approach in the Heisenberg picture, or formulation, in which the observable and other operators are time-dependent whereas the state vectors is called the Hamiltonian operator, H, and only very rarely the Schrödinger operator. The energy conservation (quantum) law written with the operator H as the Schrödinger equation is fundamental in quantum mechanics and is perhaps the most utilized, mathematical computation device in quantum mechanics of systems with a finite number of degrees of freedom. There is also, however, the alternative approach in the Heisenberg picture, or formulation, in which the observable and other operators are time-dependent whereas the state vectors  are time-independent, which reverses the time dependences betwen operators and state vectors from the more popular Schrödinger formulation. Other formulations of quantum theories occur in quantum field theories (QFT), such as QED (quantum electrodynamics) and QCD (quantum chromodynamics). are time-independent, which reverses the time dependences betwen operators and state vectors from the more popular Schrödinger formulation. Other formulations of quantum theories occur in quantum field theories (QFT), such as QED (quantum electrodynamics) and QCD (quantum chromodynamics).
Although the two formulations, or pictures, are unitarily (or mathematically) equivalent, however, sometimes the claim is made that the Heisenberg picture is âmore natural and fundamental than the Schrödingerâ formulation because the Lorentz invariance from general relativity is also encountered in the Heisenberg picture, and also because there is a `correspondence' between the commutator of an observable operator with the Hamiltonian operator, and the Poisson bracket formulation of classical mechanics. If the state vector 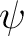 , or , or
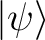 does not change with time as in the Heisenberg picture, then the `equation of motion' of a (quantum) observable operator is : does not change with time as in the Heisenberg picture, then the `equation of motion' of a (quantum) observable operator is :
|
"quantum Hamiltonian operator" is owned by bci1.
|
|
See Also: wave equation, Hamiltonian algebroid, Quantum operator algebras in QFT, Observables and States
| Other names: |
hamiltonian, Hamiltonian operator |
| Also defines: |
Hamiltonian operator, Hamiltonian, Schrödinger operator, Hamiltonian, Heisenberg's quantum approach or picture |
| Keywords: |
hamiltonian operator, Schrödinger operator |
Cross-references: motion, classical mechanics, commutator, general relativity, QCD, quantum electrodynamics, QED, QFT, quantum theories, operators, observable, systems, computation, energy, function, operator, Hilbert space, quantum mechanics
There are 31 references to this object.
This is version 6 of quantum Hamiltonian operator, born on 2008-10-03, modified 2009-06-22.
Object id is 301, canonical name is QuantumHamiltonianOperator.
Accessed 3781 times total.
Classification:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pending Errata and Addenda
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

