|
qubit and qudit
|
(Definition)
|
|
|
Whereas in a classical computer the bit is the unit of information, in a quantum device called a quantum computer–which is a special type of quantum automaton– this is replaced by a corresponding concept called qubit.
Definition 0.1 A qubit, qbit or quantum bit is defined as the unit of quantum information which is contained in a quantum state vector for a two-level quantum system consisting of only two energy levels; mathematically this is expressed as a unit vector 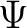 in a a two-dimensional vector space
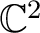 over the field of complex numbers
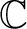 .
In order to have any practical use such a qubit must also meet several conditions, such as: it has to be measurable, undergo controlled unitary transformations, have a long coherence time, be capable of initialization, and so on. Scalability to a quantum state space
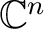 of of
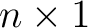 column vectors with the inner product column vectors with the inner product
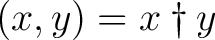 is also such a condition, where is also such a condition, where
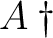 denotes the transpose conjugate of denotes the transpose conjugate of 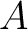 . Then a unit vector . Then a unit vector 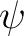 in in
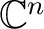 denotes a quantum state. As an example, in a superconducting flux qubit an electric current can be imagined to circulate simultaneously in a stable (or coherent) loop both clockwise and counterclockwise. A qubit in such a superposition is in a highly symmetrical quantum state. Superconducting qubits involve large numbers of particles (Cooper pairs) as the superconducting current involves many billions of such coherent electron pairs. In such a many-particle superconducting loop, spontaneous symmetry breaking tends to determine the qubit to end up in a definite state, by `breaking up the superposition'. On the other hand, an ion suspended in a magnetic trap or a single electron in a quantum dot on a chip do not
exhibit this phenomenon. In August 2005, a group of physicists at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) suceeded in preparing single-ion qubits with a coherence time longer than 10 seconds. denotes a quantum state. As an example, in a superconducting flux qubit an electric current can be imagined to circulate simultaneously in a stable (or coherent) loop both clockwise and counterclockwise. A qubit in such a superposition is in a highly symmetrical quantum state. Superconducting qubits involve large numbers of particles (Cooper pairs) as the superconducting current involves many billions of such coherent electron pairs. In such a many-particle superconducting loop, spontaneous symmetry breaking tends to determine the qubit to end up in a definite state, by `breaking up the superposition'. On the other hand, an ion suspended in a magnetic trap or a single electron in a quantum dot on a chip do not
exhibit this phenomenon. In August 2005, a group of physicists at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) suceeded in preparing single-ion qubits with a coherence time longer than 10 seconds.
Definition 0.2 A qudit is defined as the unit of quantum information in a 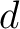 -level quantum system
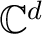 which is contained in the unit vector in a vector space
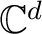 of dimension 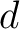 .
Furthermore, one can define as follows a more complex concept than the qudit by allowing for entanglement of quantum states.
Definition 0.3 A quantum register
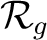 consists, or is determined by, a number 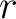 of entangled qubits.
Quantum computers could then perform calculations by manipulating qubits within a quantum register. However, the requirement for long coherence times may be a major obstacle to building quantum computers [1].
- 1
- Graham P. Collins.,October 17, 2005, Quantum Bug: Qubits might spontaneously decay in seconds. Scientific American
|
"qubit and qudit" is owned by bci1.
|
|
See Also: quantum solitons, quantum automata, quantum circuit
| Also defines: |
qubit, quantum computer, quantum bit, qudit, quantum register, single-ion qubits, coherence time, NIST, quantum dot on a chip, Cooper pair, superconducting loop, superconducting flux qubit, n-level quantum system, two-level quantum system |
| Keywords: |
quantum computer, quantum bit, bit, quantum automaton |
Cross-references: quantum computers, system, group, spontaneous symmetry breaking, Cooper pairs, inner product, vectors, quantum state space, field, vector space, two-dimensional, unit vector, energy, state vector, concept, type, computer
There are 2 references to this object.
This is version 13 of qubit and qudit, born on 2009-05-04, modified 2009-09-10.
Object id is 732, canonical name is Qubit2.
Accessed 8289 times total.
Classification:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pending Errata and Addenda
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

